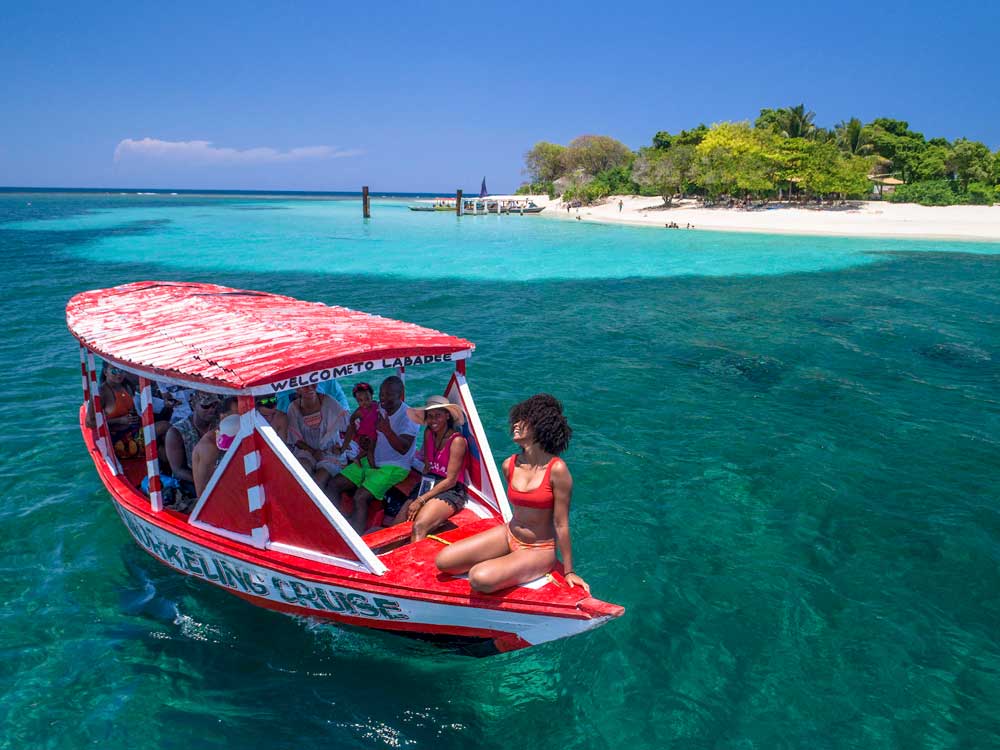
Photo: Jean Oscar Augustin
Entry to Haiti: Visa & Travel Requirements
Navigate Haiti’s entry process and visa requirements with ease
Haiti is a nation famed for its rich history and stunning beaches, attracts travelers from around the world. Yet, the lack of clear online information, leaves many travelers confused regarding the specific entry requirements and the need for tourist visas, often leading to uncertainty and potential travel complications.
So, what exactly are the visa policies for Haiti, and what should you know before embarking on your journey?
This article is your essential guide, detailing Haiti’s visa and travel requirements, including up-to-date vaccination information and safety tips, to help you prepare thoroughly for an unforgettable Haitian experience.

Photo: Dyerlin Delva
Visa requirement for tourist
For stays under three months, tourists from most countries, including the U.S., Canada, and Europe, can enjoy Haiti’s beauty without the need for a tourist visa. A notable exception applies to nationals from the Dominican Republic, Panama, Colombia, Cuba, Syria, Libya, Vietnam, or Yemen, who must obtain a visa beforehand.
Importantly, upon arrival in Haiti, all tourists are required to pay an entry fee of $10 USD. Please note, this fee must be paid in cash at the airport as credit cards are not accepted. To ensure your entry is as smooth as your flight, keep some cash handy for this fee.
For an extended stay in Haiti
Planning to extend your journey in Haiti beyond 90 days? It’s essential to apply for a residence permit. This step is required for all visitors who wish to stay in Haiti for a longer period, or are considering making Haiti their permanent home. Start the application process at one of Haiti’s 26 embassies or through any of its 19 consulates abroad.
Remember, you’ll need to have a valid passport and all necessary documents as outlined by your nearest Haitian embassy.
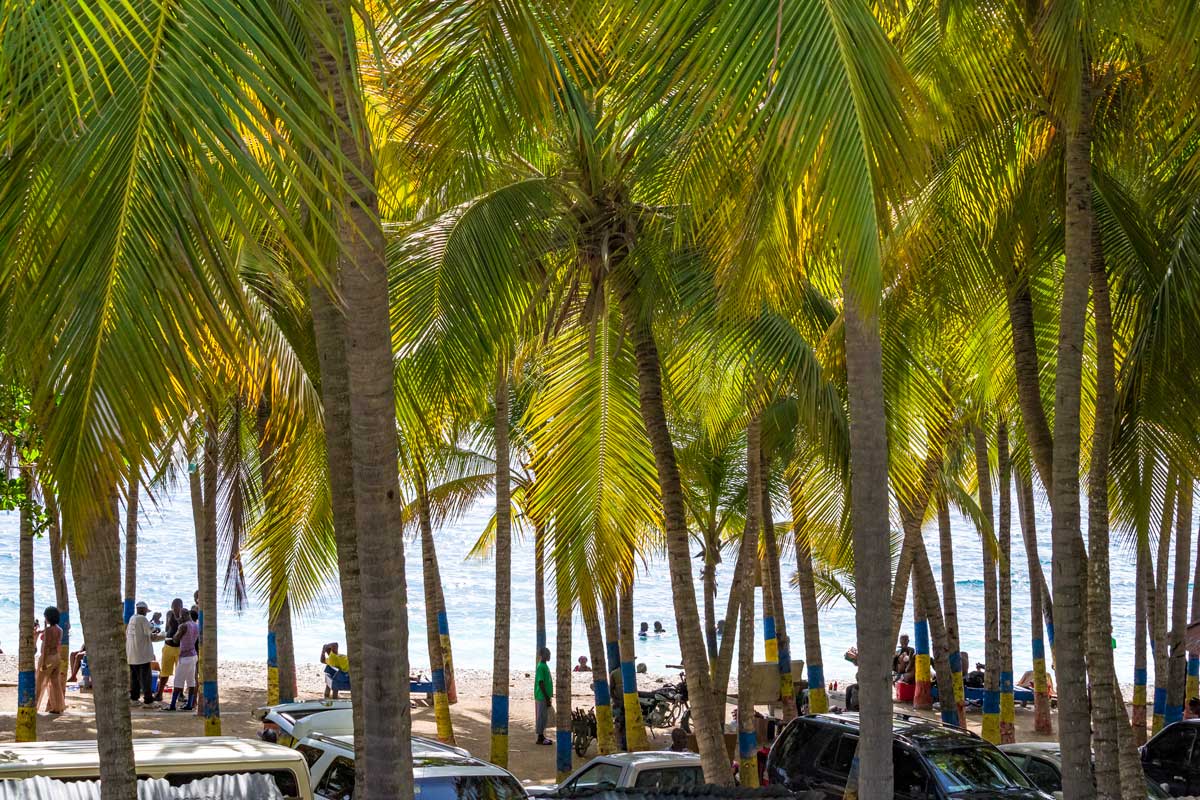

Photo: Verdy Verna
Prohibited items for travels to Haiti
This includes not only the obvious – firearms, weapons, explosives, drugs, and narcotics – but also materials of a pornographic nature or those considered contrary to good morals. Also, be mindful of the duty-free allowances for tobacco products and alcohol, and for specific details, consult your local Haitian embassy.
To help ensure your journey is hassle-free, our comprehensive What to Pack guide provides all the essential information about what to bring for your trip to Haiti.
Can i bring my pet to Haiti?
Want to bring your furry friend along to Haiti? Absolutely, you can! Just ensure your pet isn’t on the endangered species list or subject to international transport restrictions. In Haiti, pets can accompany you either as part of your checked luggage or shipped via cargo. Don’t forget the essential paperwork – a travel certificate and a valid medical certificate are a must for your pet’s journey. For specific guidelines and any additional requirements, it’s a good idea to check with your local Haitian consulate or embassy before travel.
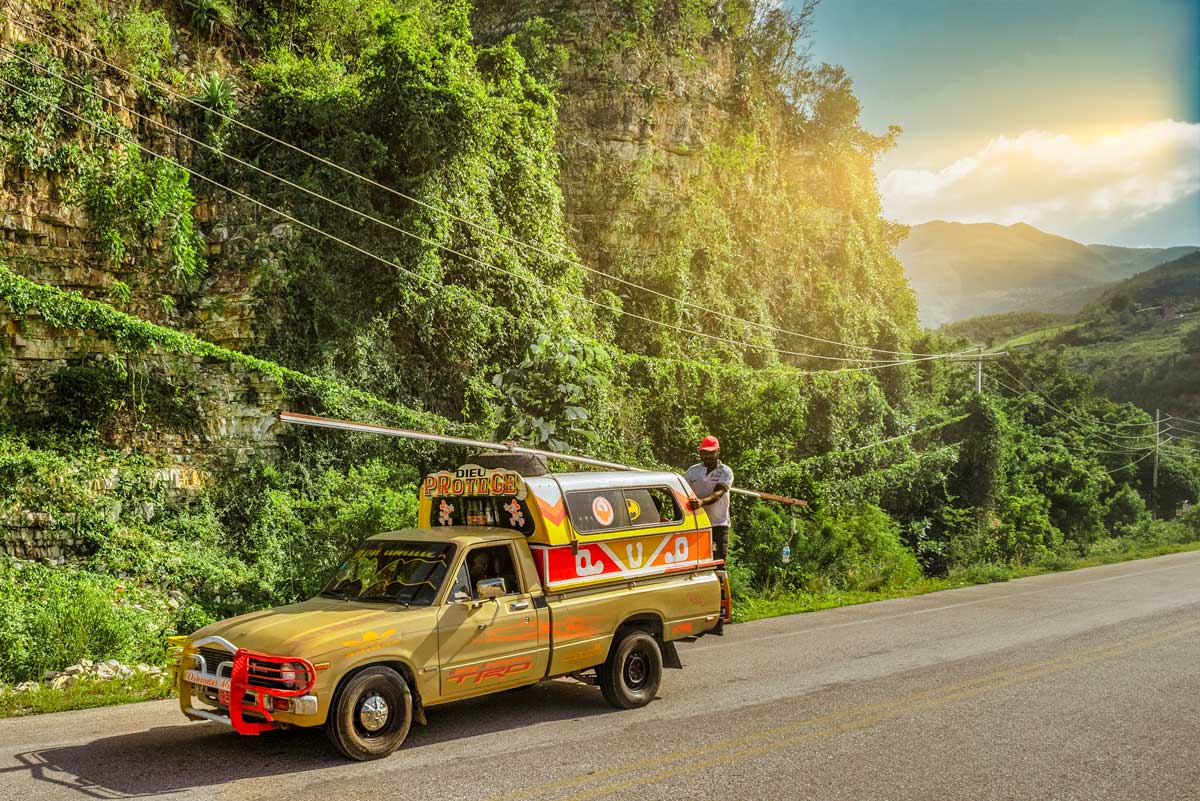

Photo: Jean Oscar Augustin
Vaccination requirements for Haiti
Before traveling to Haiti, ensure you are vaccinated against Covid-19, as this is a mandatory requirement. While other vaccinations are optional, remember that Haiti’s tropical climate can increase the risk of mosquito-borne infections. To safeguard your health, consider getting vaccinated against tropical diseases like yellow fever and dengue. Make sure you’re up to date with routine vaccines for diphtheria, tetanus, chickenpox, and polio.
If your adventure includes exploring rural areas or nature, vaccinations for rabies, Hepatitis, and cholera are recommended. Always check with your local healthcare provider for the latest health risk information and vaccination requirements.
Don’t forget to read our article on how to stay healthy and safe while enjoying the beauty of Haiti!
Written by Costaguinov Baptiste.
Published November 2023.
Get to Know Haiti a Little Better

Paradise for your inbox
Your monthly ticket to Haiti awaits! Get first-hand travel tips, the latest news, and inspiring stories delivered straight to your inbox—no spam, just paradise.