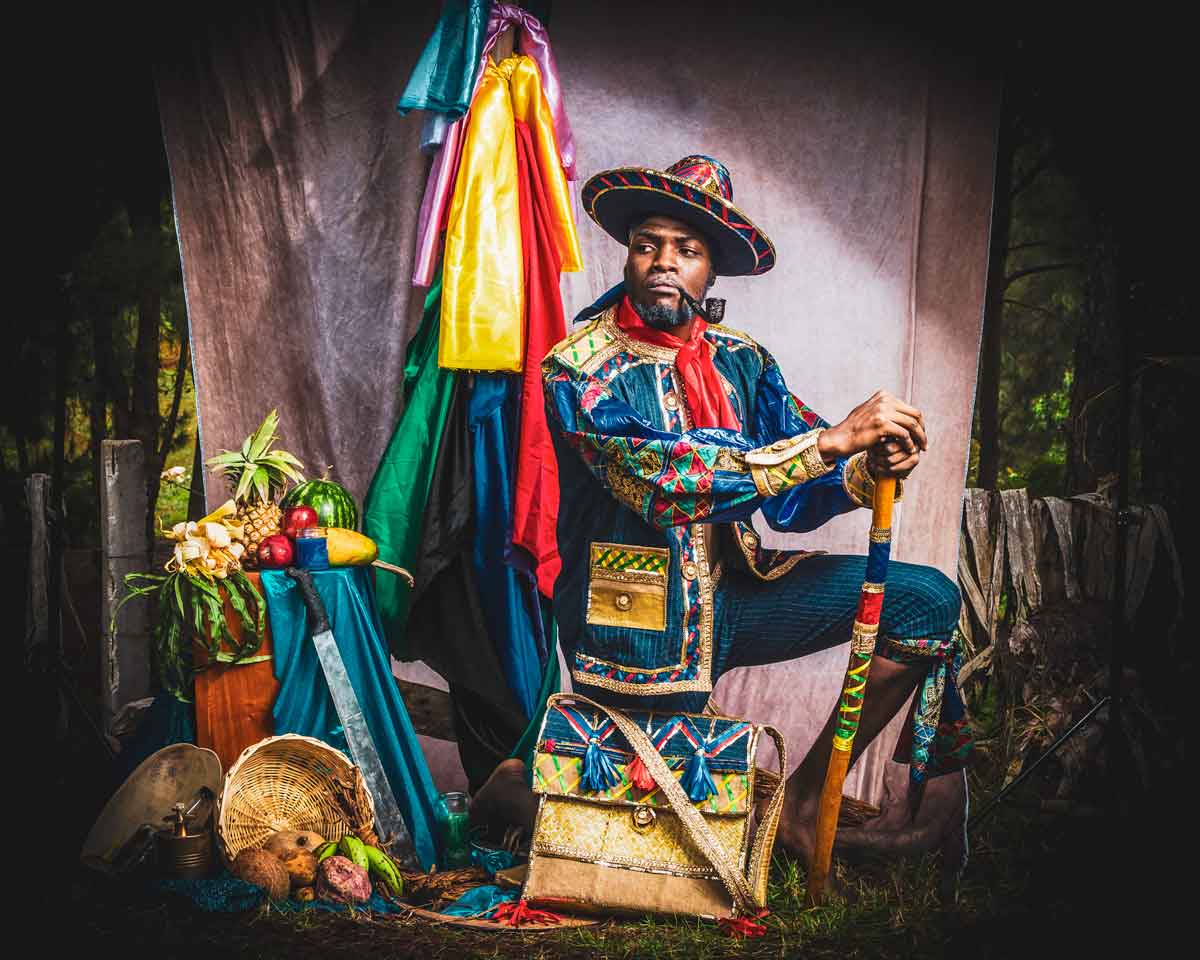
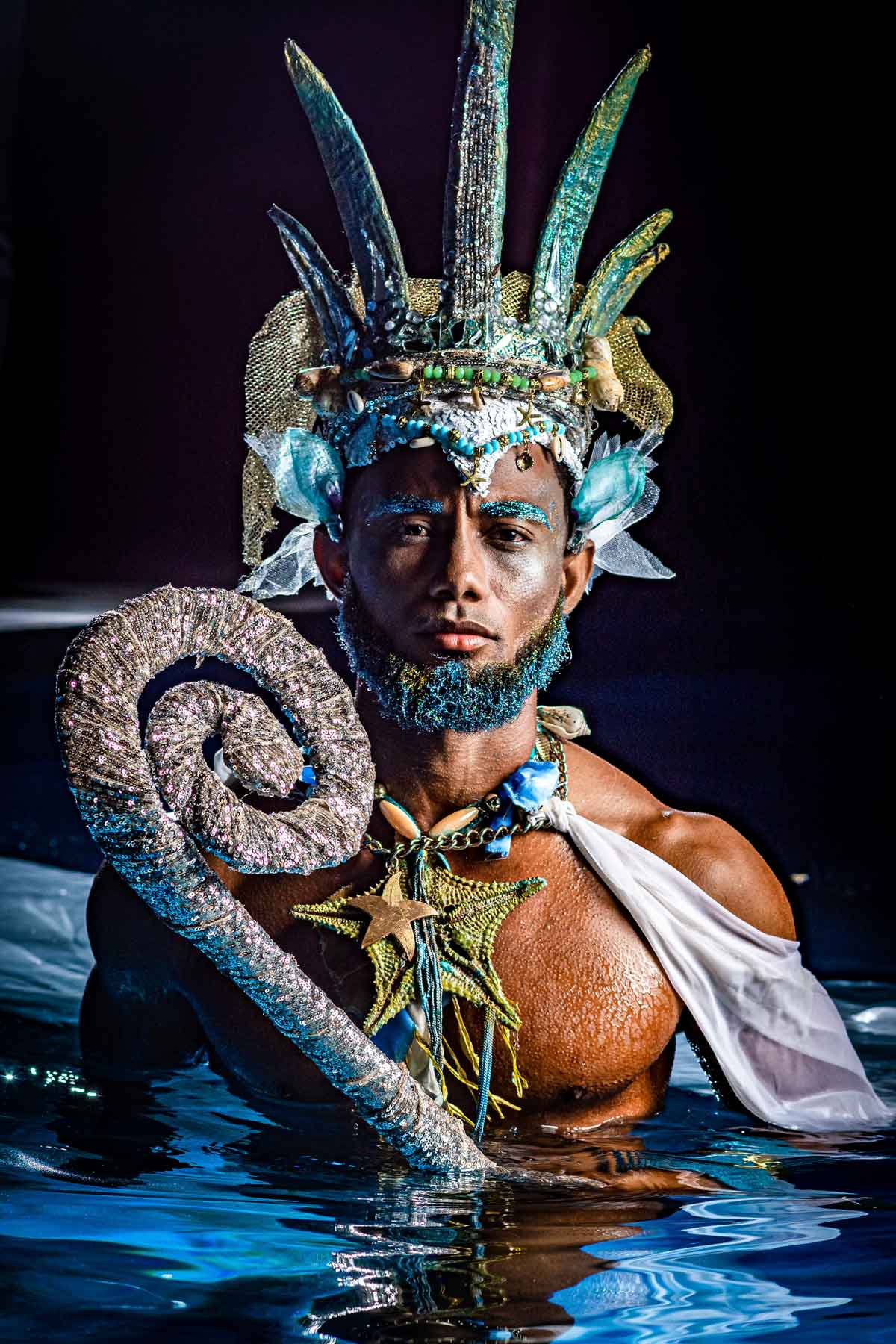
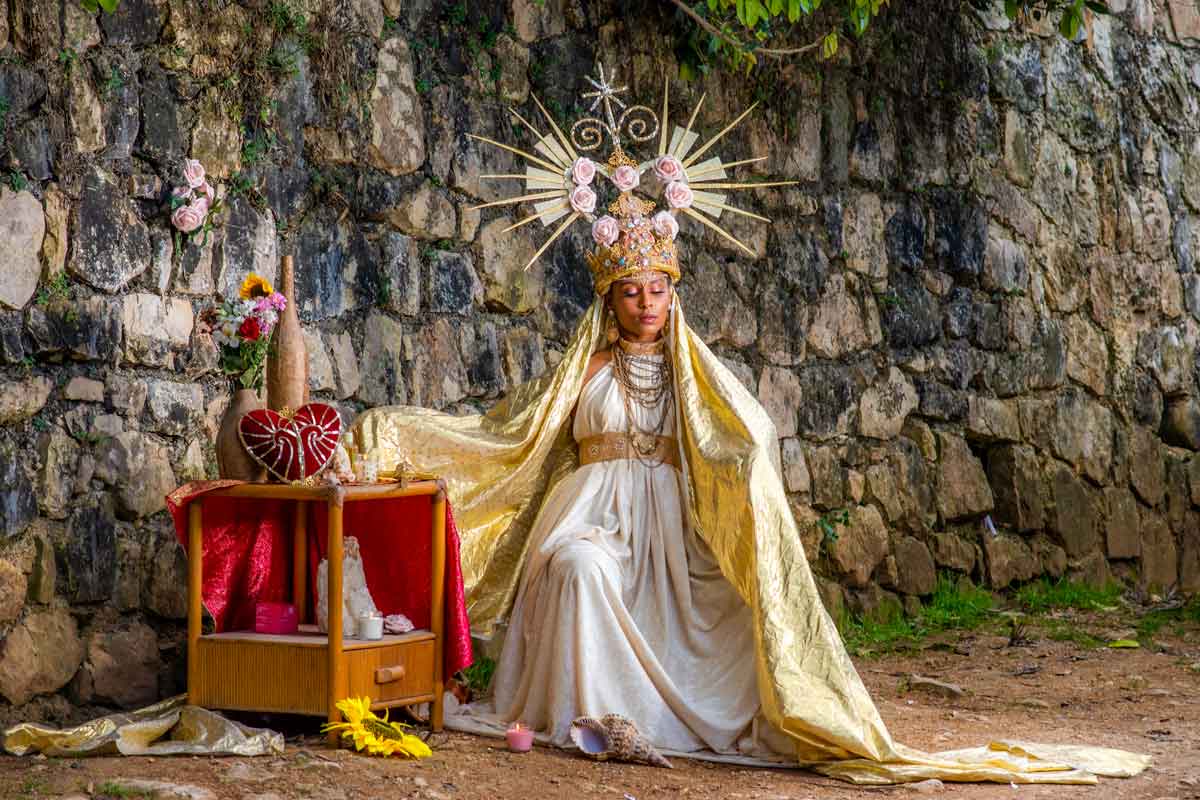
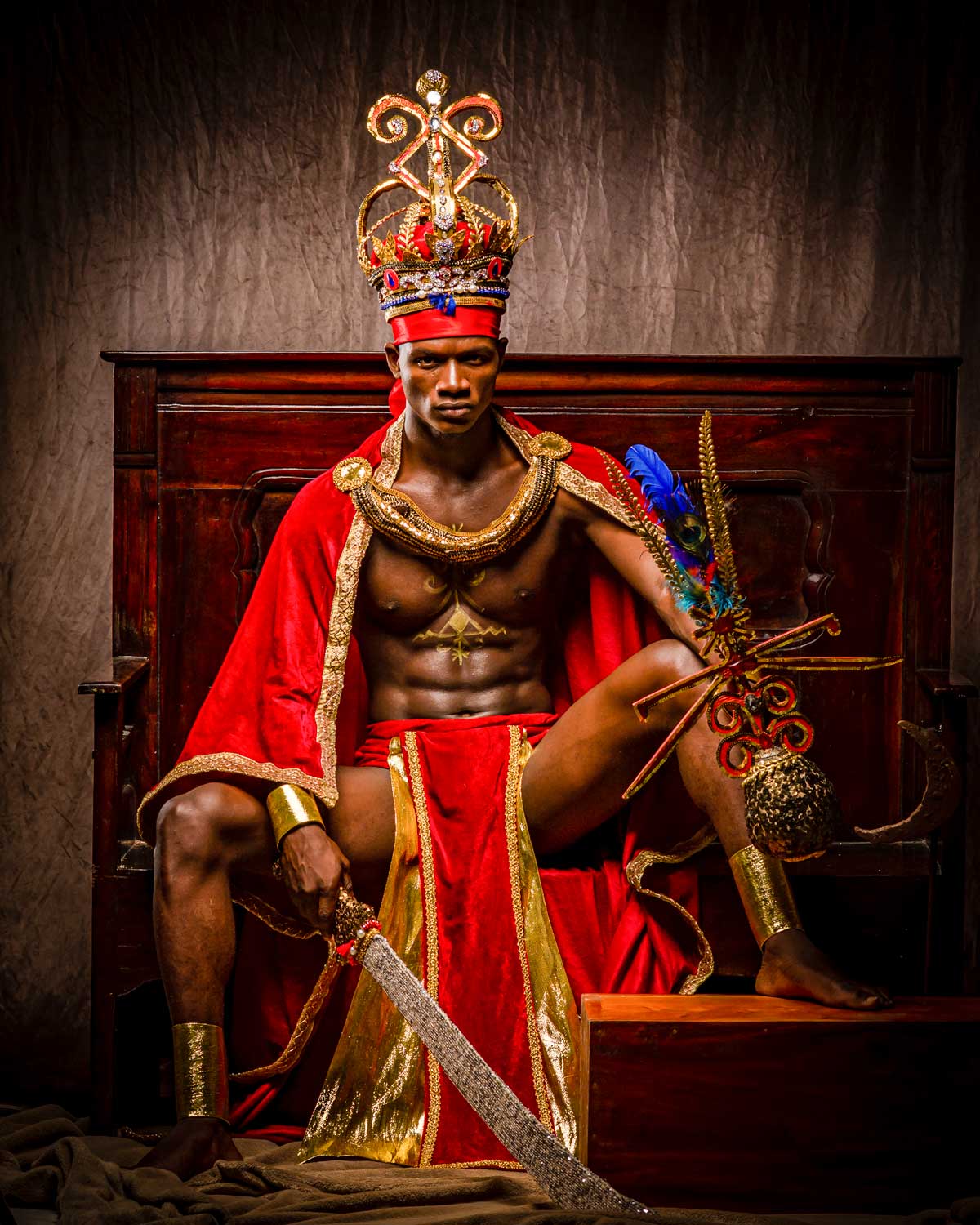
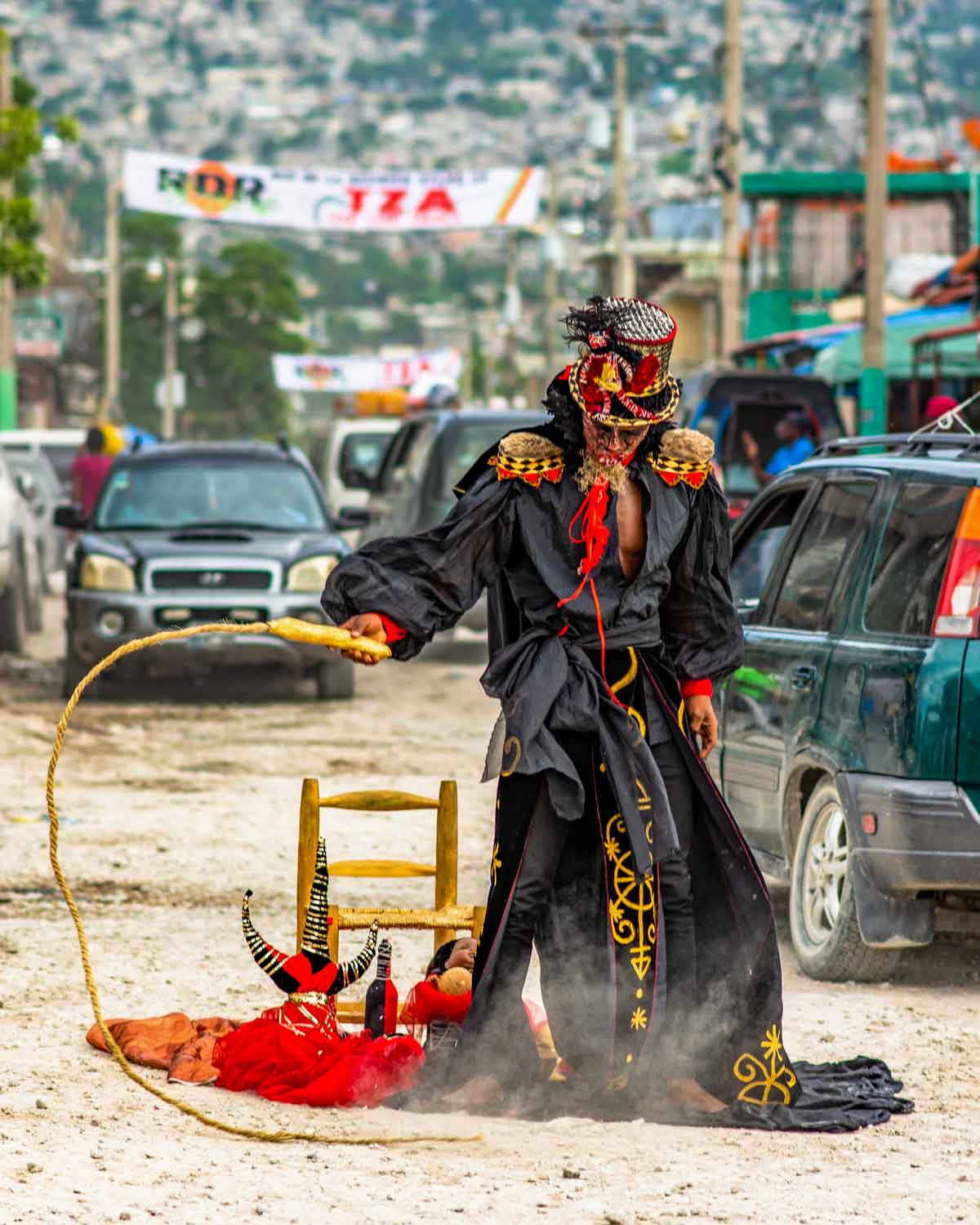
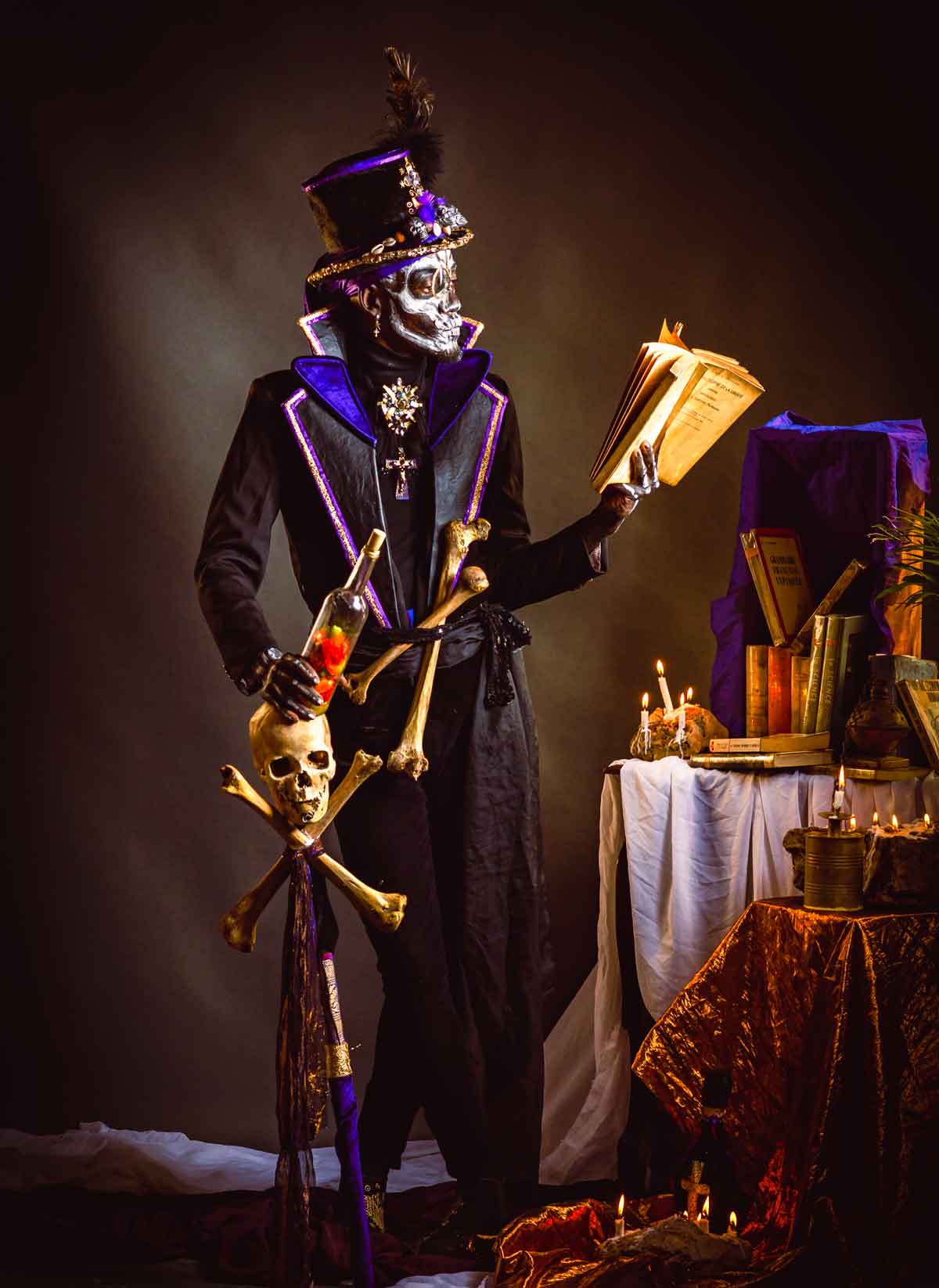
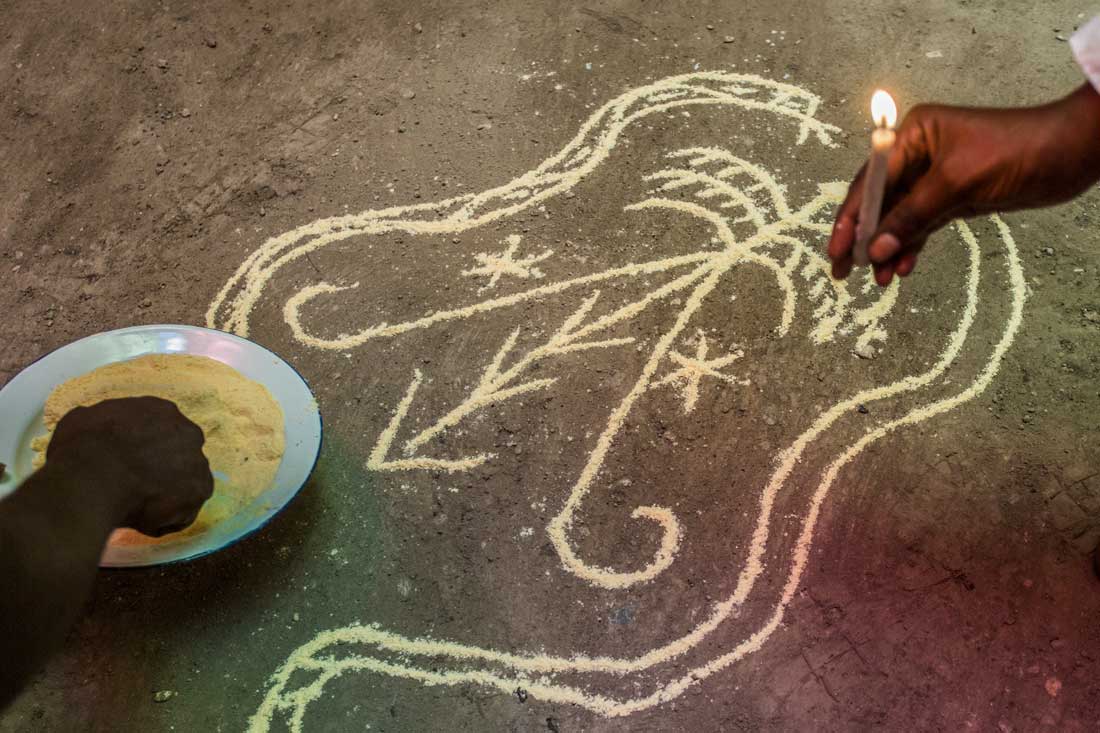Photo: Pierre Michel Jean
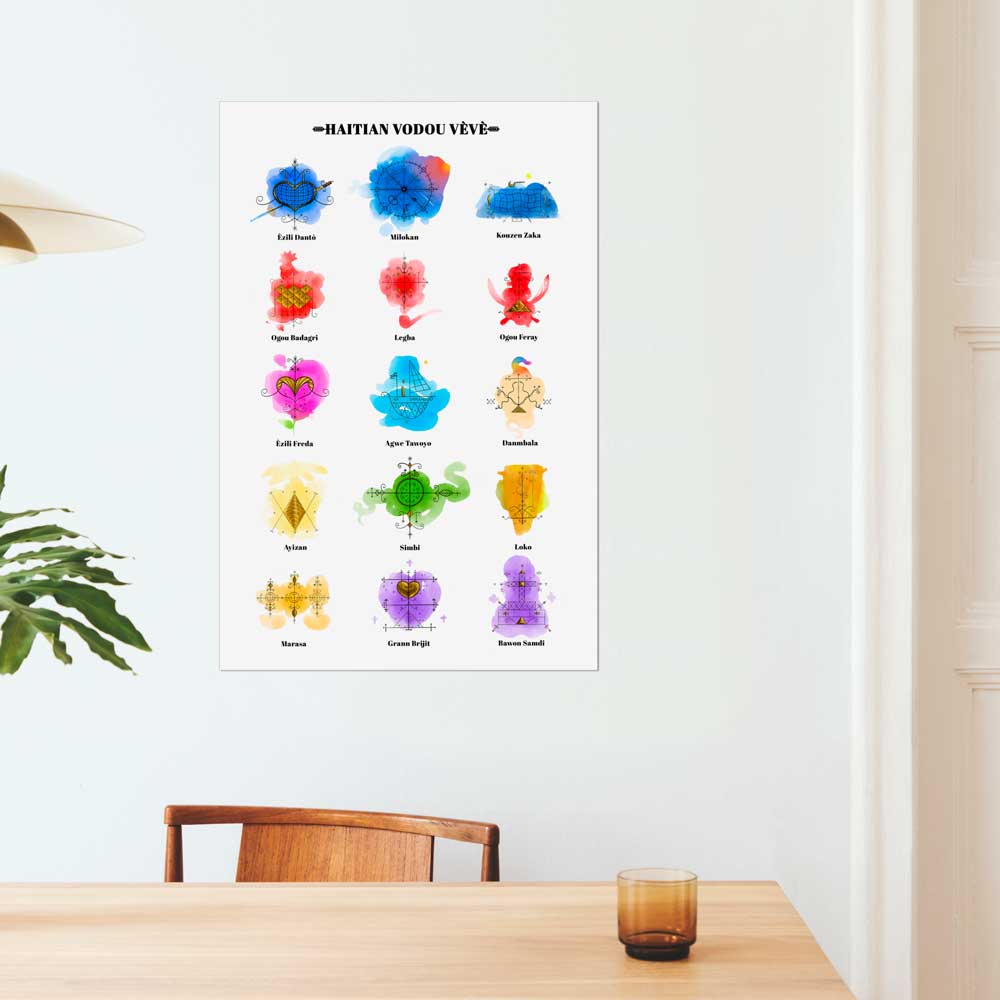
A Visual Guide to Vèvè: Vodou Symbols & Cosmograms
Discover the intricate art of Vodou symbols with our visual guide to the vèvè of Haitian Vodou. Immerse yourself in the heart of spirituality and tradition and learn the significance behind each symbol.
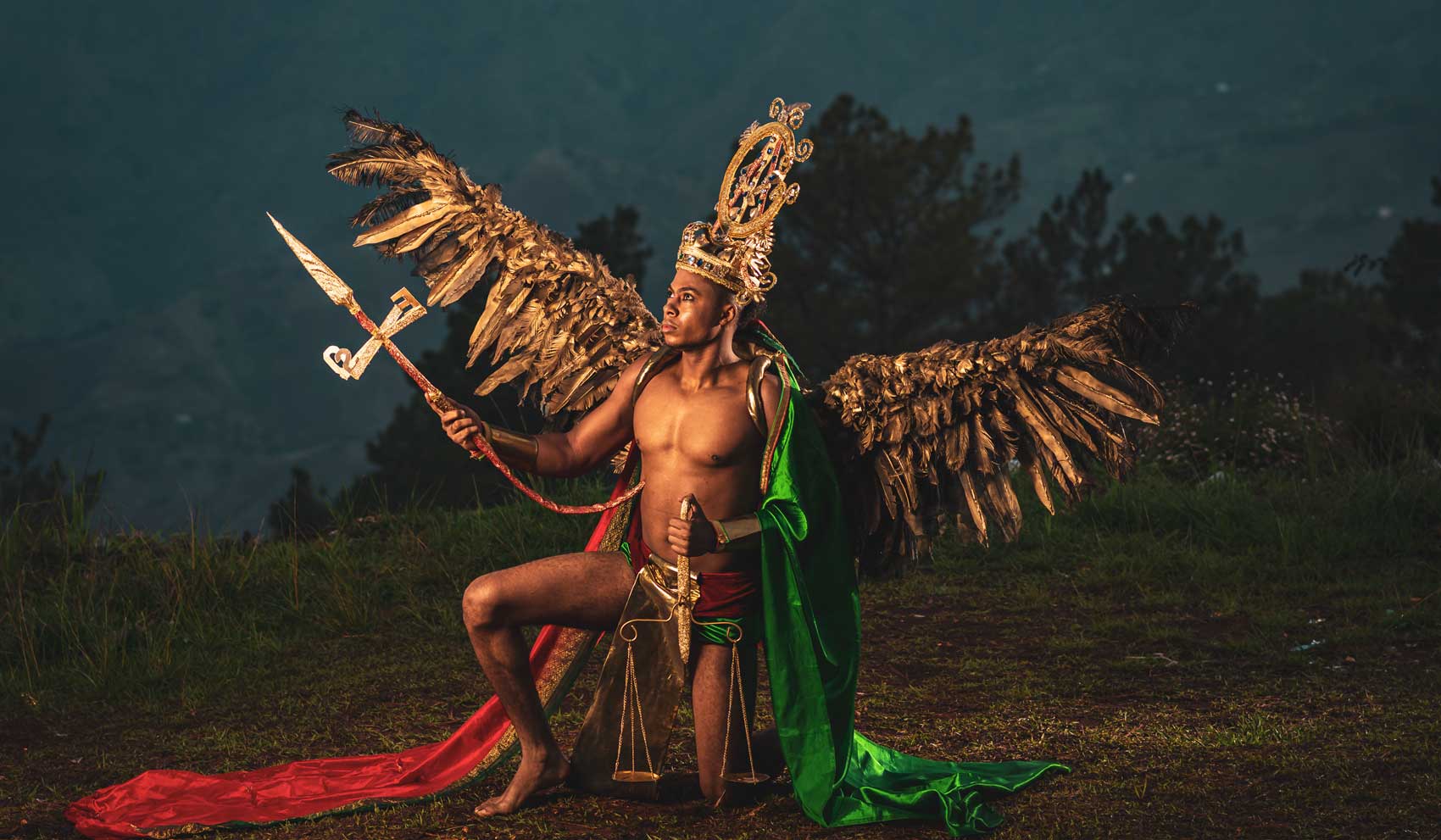
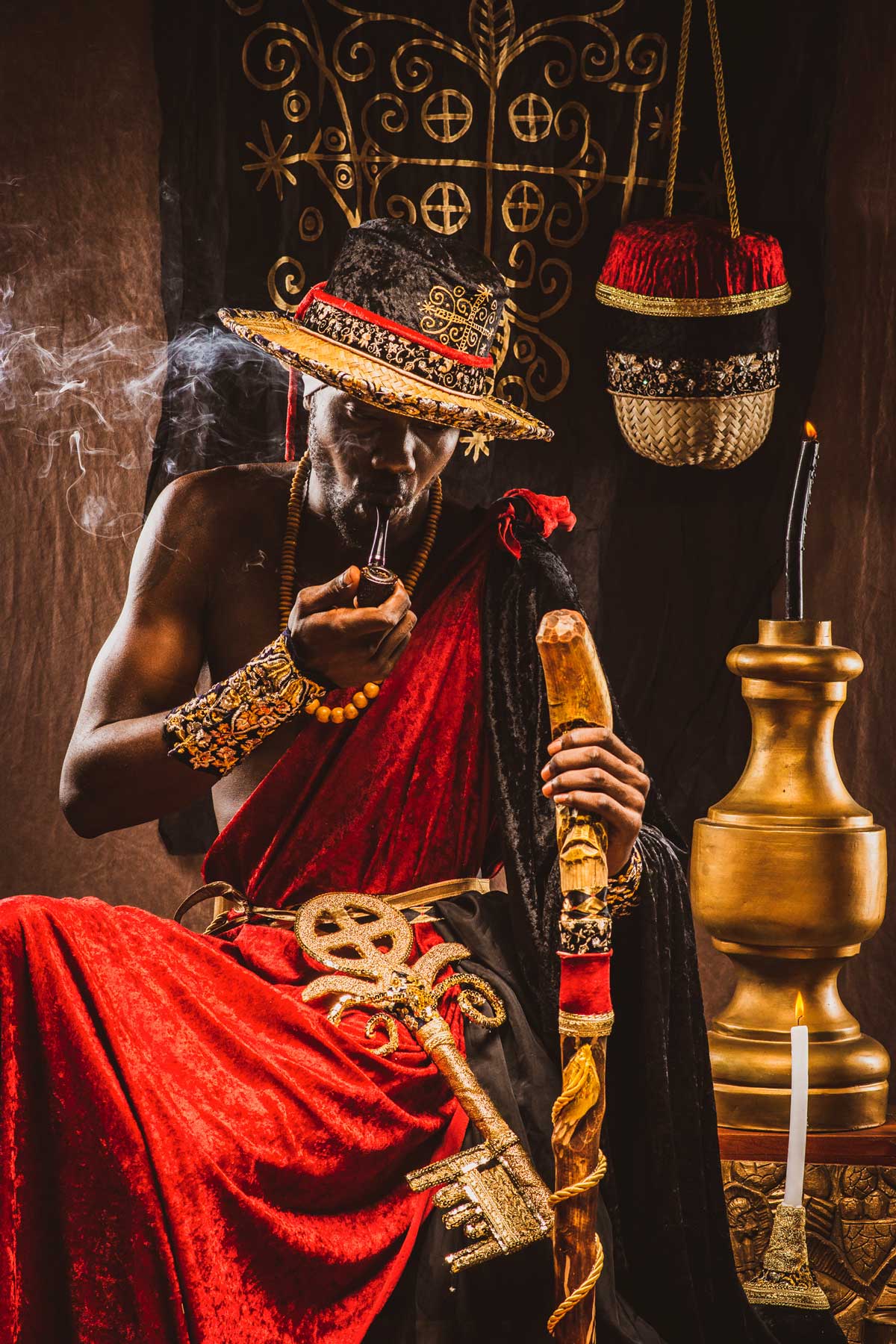
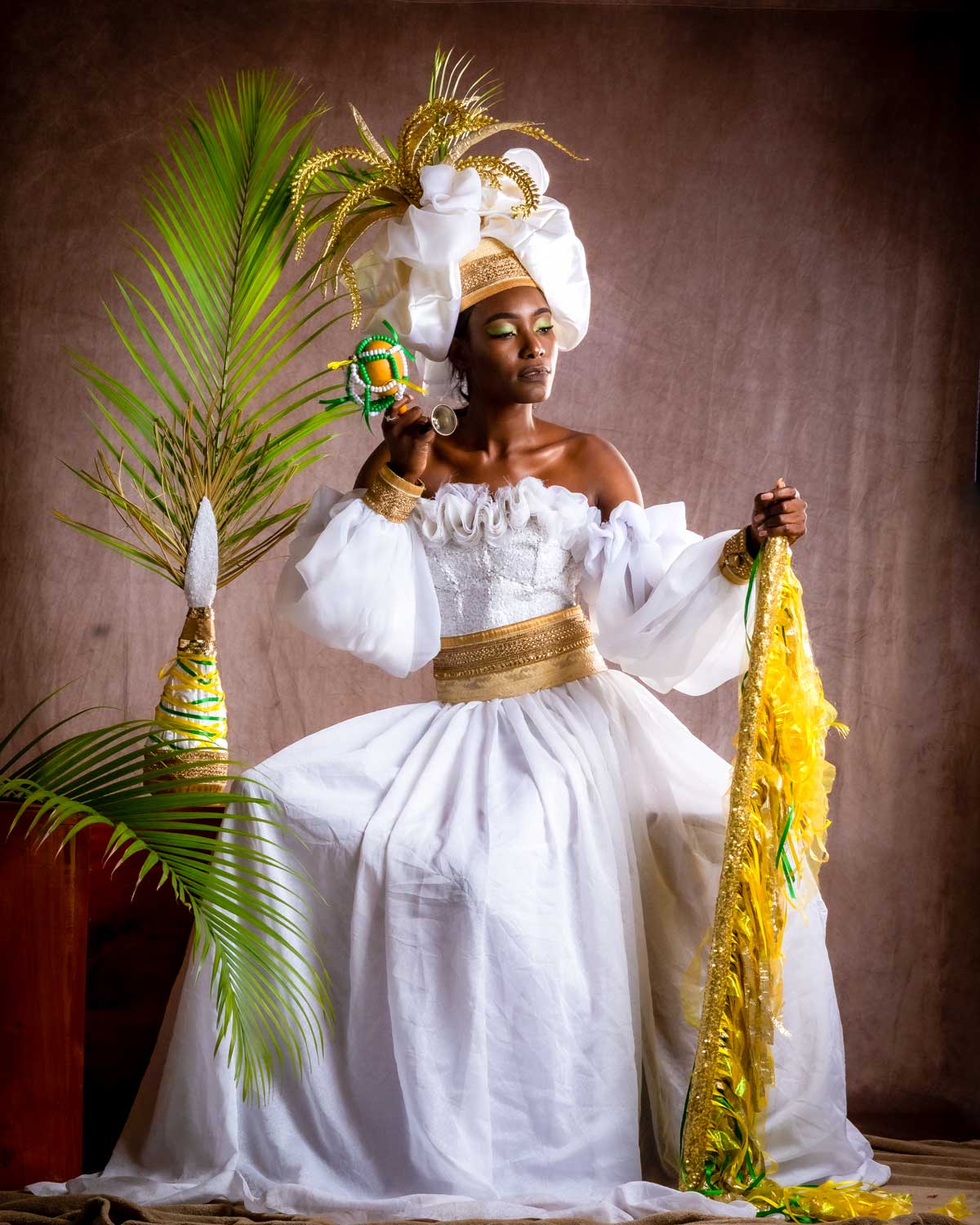
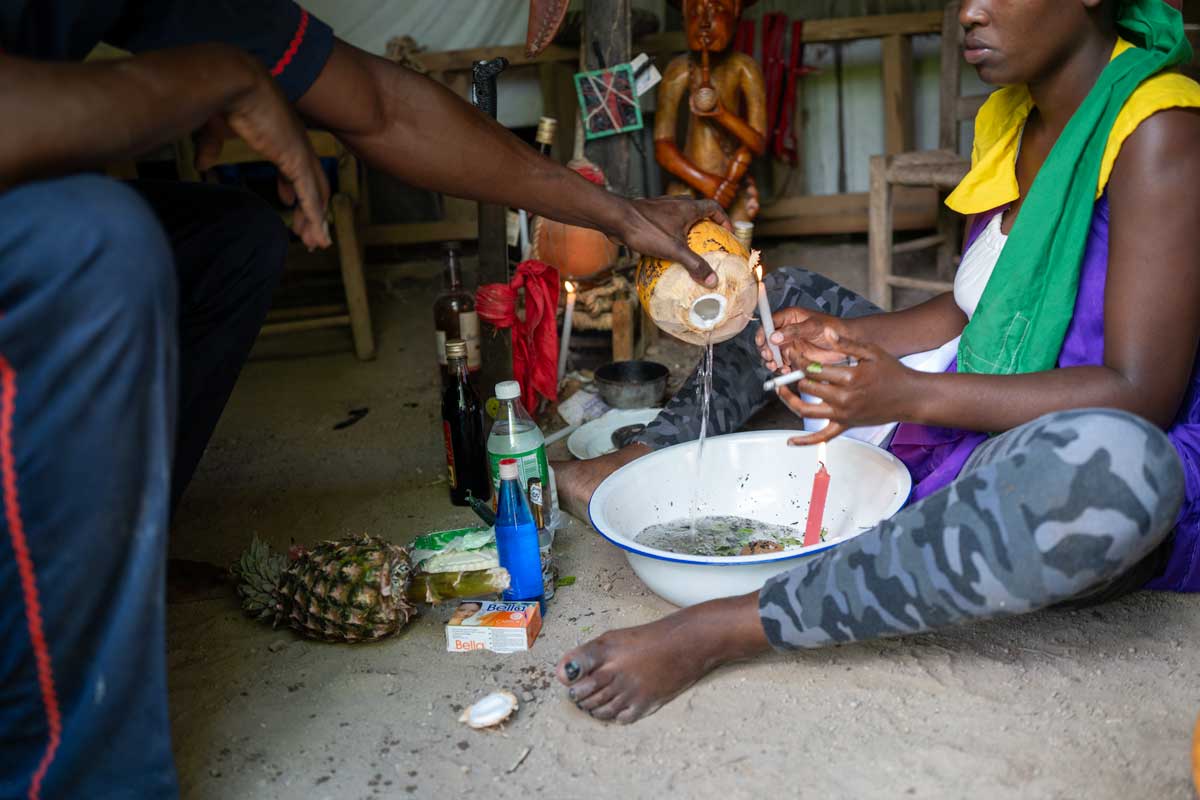
Vodou, a spiritual and cultural practice that has long intrigued people from around the world, is a fascinating blend of African, Native American, and European beliefs and traditions. It’s a rich tapestry woven from the beliefs and experiences of enslaved peoples brought to the Caribbean and the Americas, and it has been shaped and evolved over centuries to become what it is today.
At the heart of Vodou are the symbols known as vèvè. These cosmograms are intricate drawings made with cornmeal, coffee, or flour, and they serve as the visual representation of the spirits and deities honored in Vodou. Each vèvè corresponds to a specific spirit, and invoking them involves drawing the corresponding symbol on the ground. This is often performed by an initiate who has learned the technique and is an essential part of Vodou rituals and ceremonies.

Photo: Pierre Michel Jean
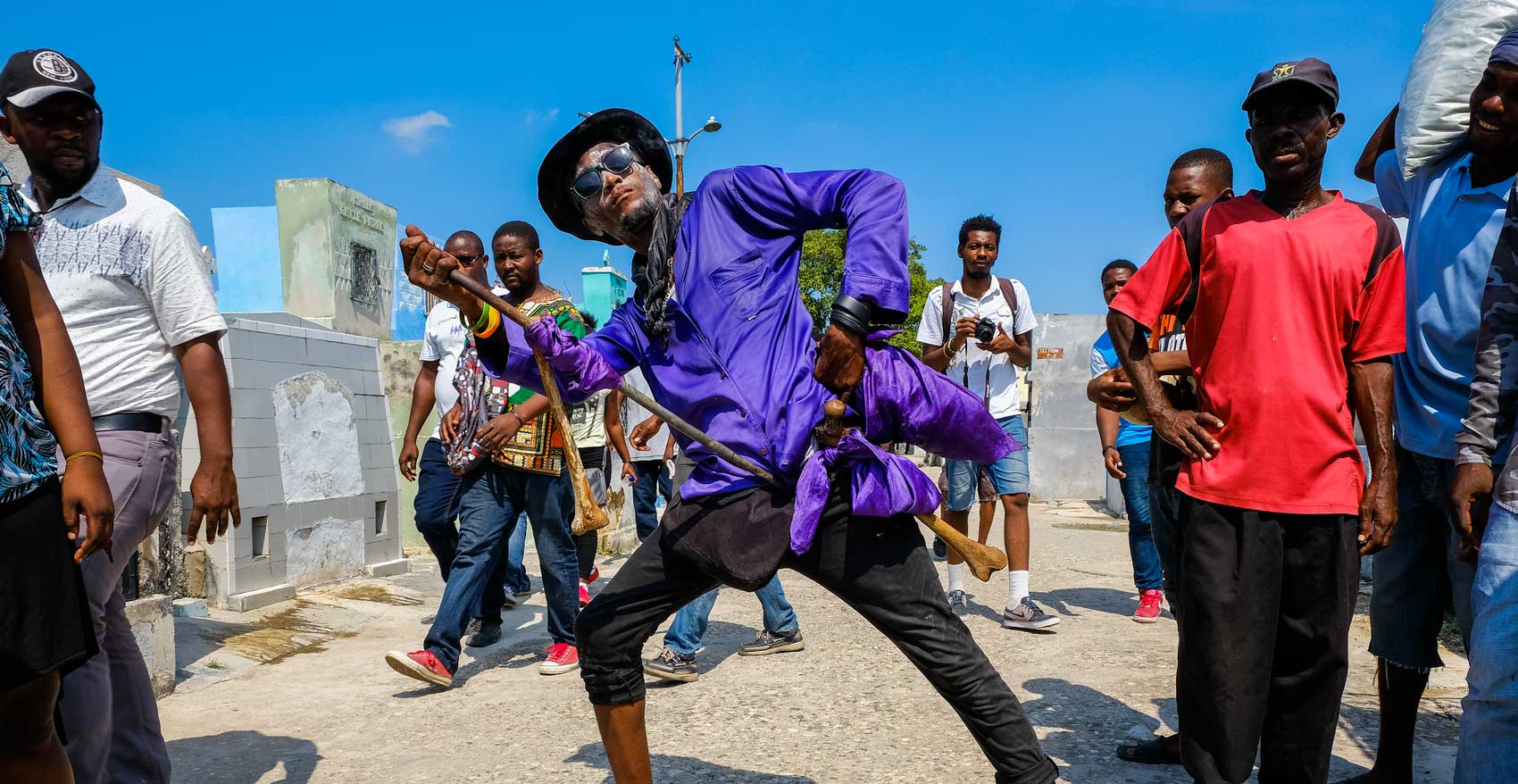
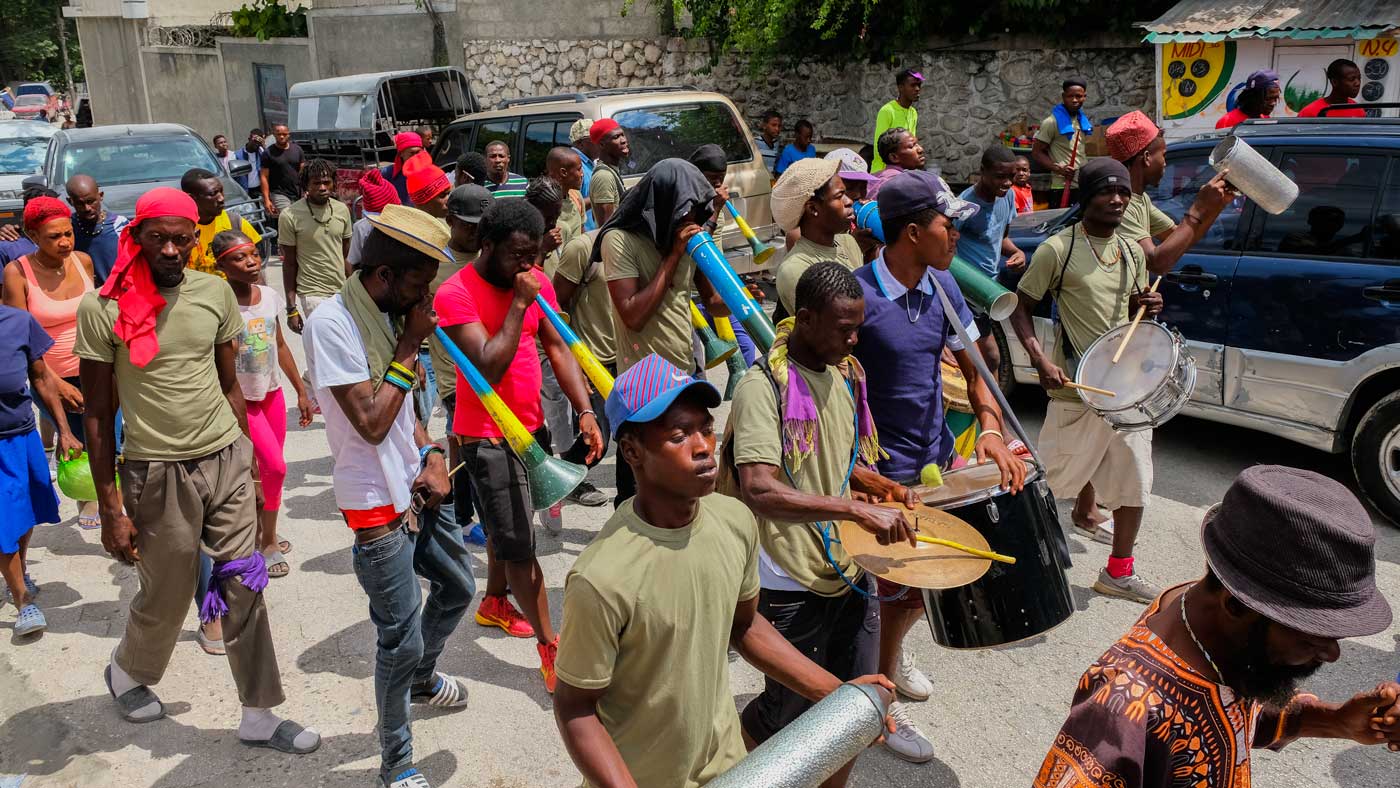
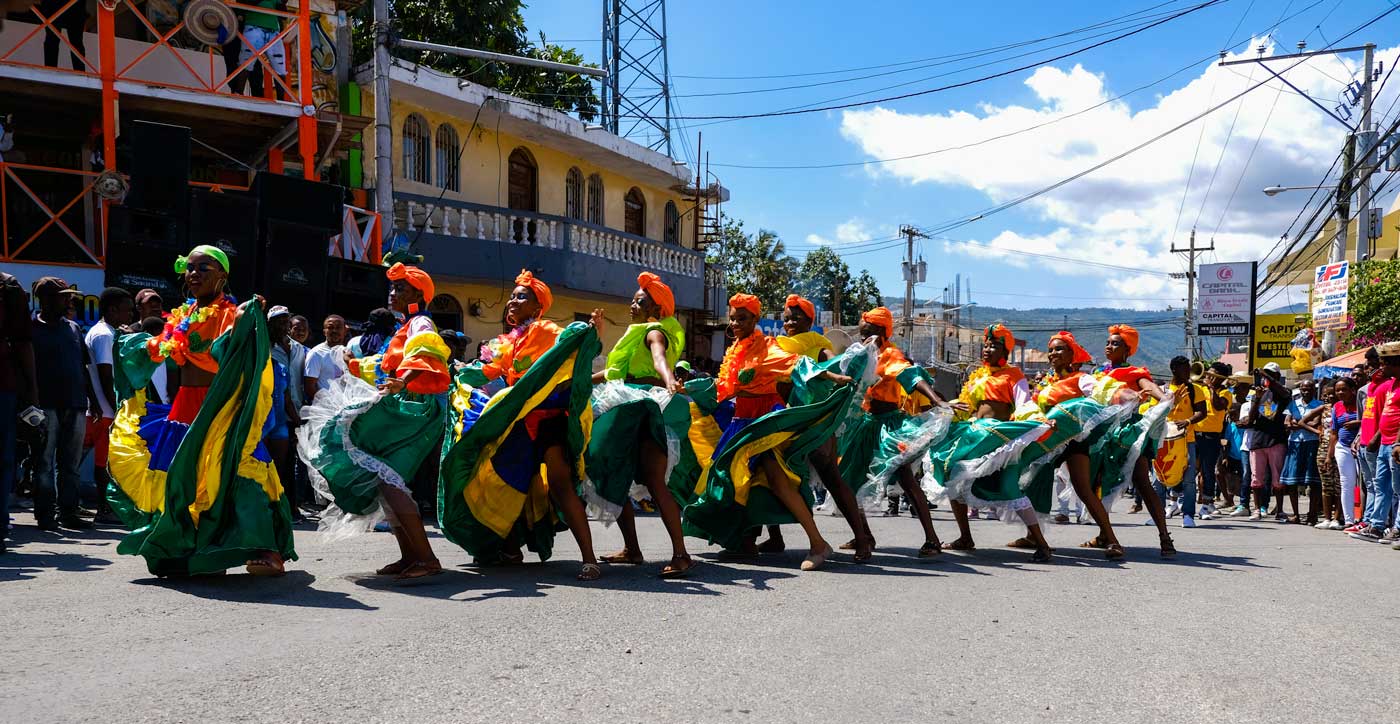
In Haiti, Vodou is a vibrant and influential part of the country’s culture, and its vèvè cosmograms are a reflection of the rich diversity of spirits and beliefs that make up this unique practice.
From the healing spirit of Simbi, guardian of rivers and sources, to the fierce and far-reaching power of Erzulie Freda and Erzulie Dantor, each vèvè holds a special significance and meaning. These symbols are not only an important part of Vodou rituals, but they are also beloved cultural icons that are celebrated in art and designs across the country.
Come along as we navigate the vast array of spirits and symbols in Haitian Vodou with this visual guide to the most prominent vèvè you’re likely to encounter in Haiti. Explore the meaning behind these symbols and dive into the world of Vodou.
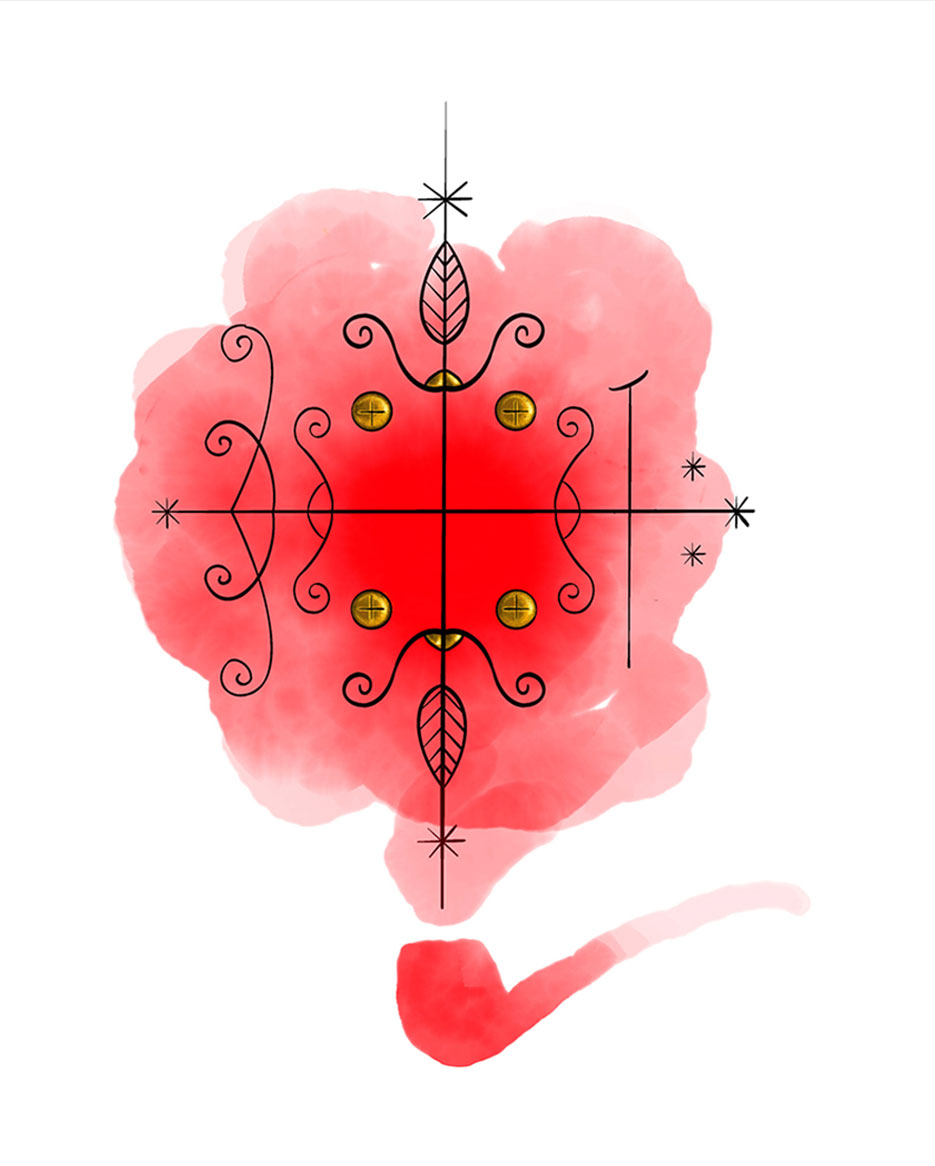
Illustration: Pyelila
Legba: The Guardian of the Gates
Papa Legba, the first spirit to manifest during a Vodou ceremony, holds a special place in the Vodou Pantheon in Haiti. He is the guardian of the gates, allowing spirits to cross into the human world. His vèvè symbolizes his role as the barrier between the two worlds, with two perpendicular axes and his cane.
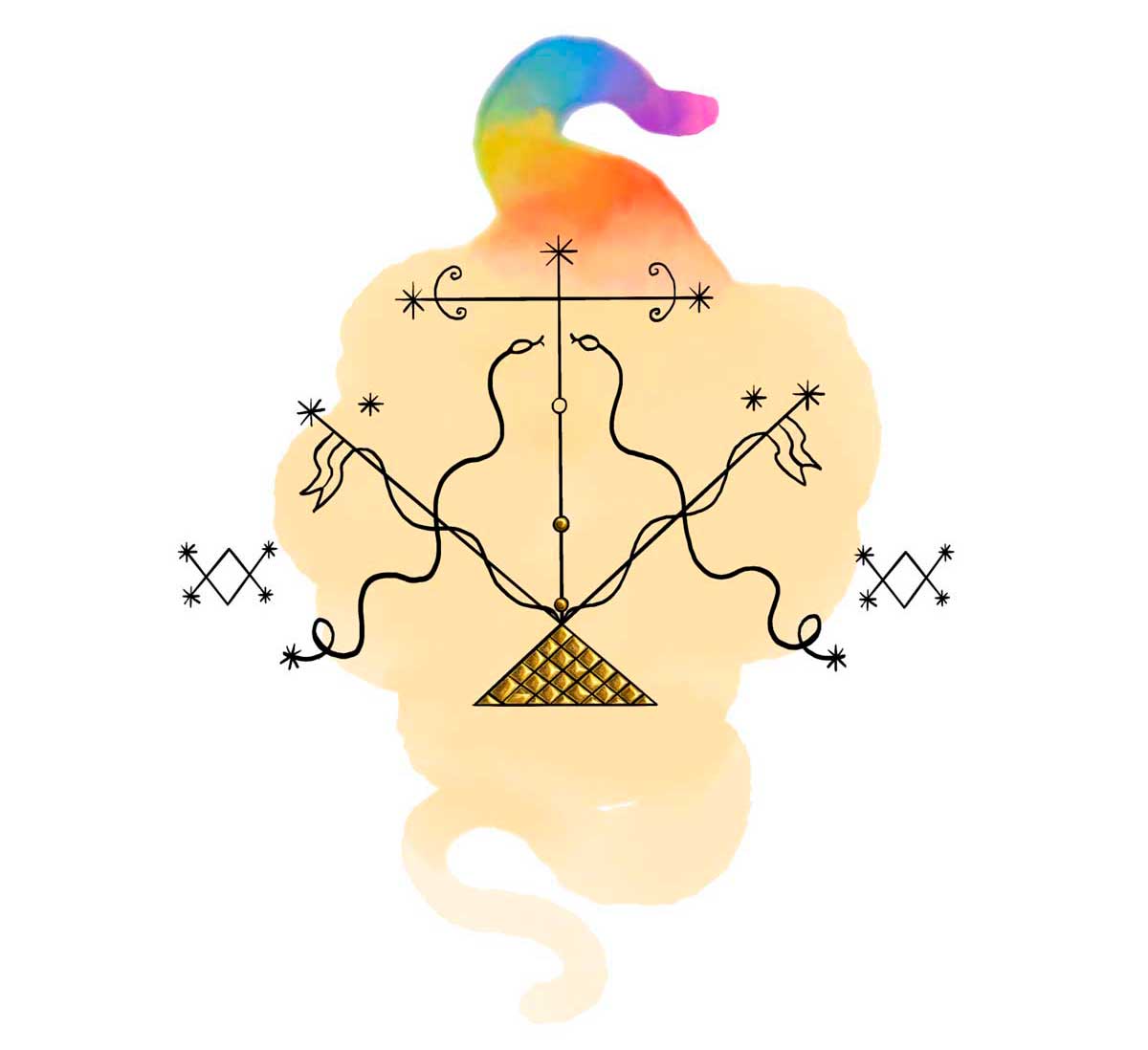
Illustration: Pyelila
Damballah and Ayida Wèdo
Papa Legba, the first spirit to manifest during a Vodou ceremony, holds a special place in the Vodou Pantheon in Haiti. He is the guardian of the gates, allowing spirits to cross into the human world. His vèvè symbolizes his role as the barrier between the two worlds, with two perpendicular axes and his cane.
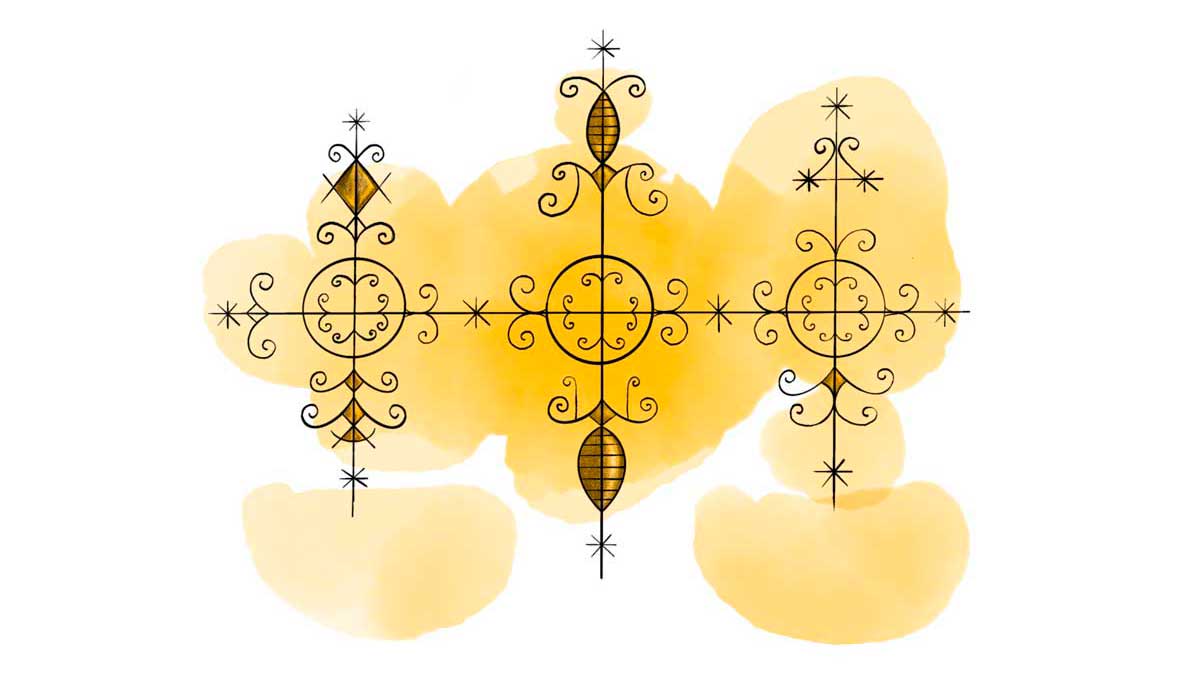
Illustration: Pyelila
Marasa: The Magical Twin Spirits
Marasa represents the duality of good and evil in Haitian Vodou. As twin spirits, they’re feared for their supposed magical powers, like the ability to control the weather and being able to predict the future. In Haiti, human twins are believed to have a strong connection, symbolized by the vèvè that shows them tied together. Marasa is often seen as mischievous, depicted as children or young adolescents in the collective imagination of Haitians.
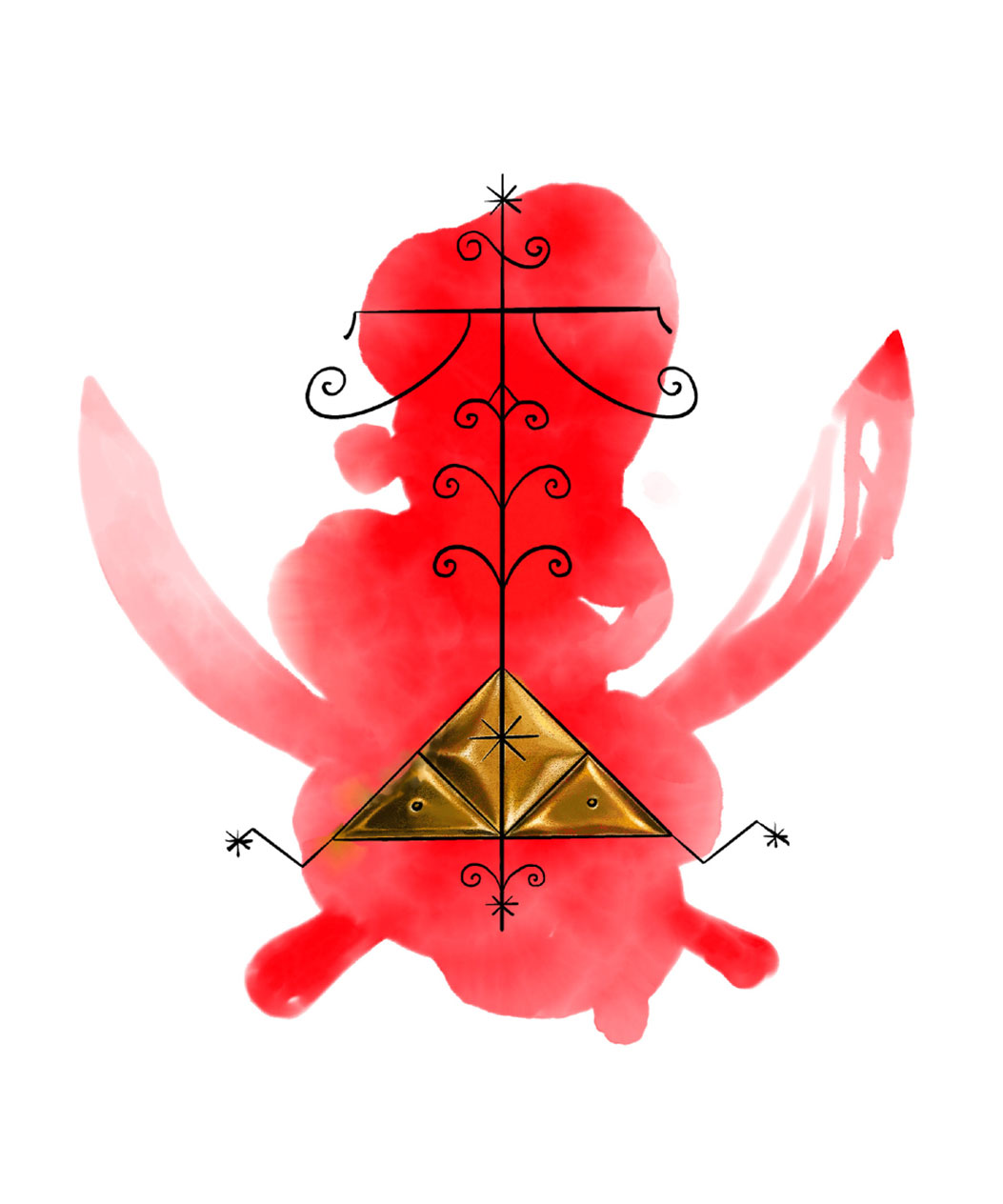

Illustration: Pyelila
Ogou: The Powerful Warrior Spirit
Ogou is a prominent spirit in the pantheon of Haitian Vodou, with several vèvè symbols dedicated to him. He is known to change his name and go by different titles, such as Ogou Feray, Ogou Badagri, and Ogou Adaché. The position of the sword in the drawing serves as a quick identifier for the different Ogous. For example, the Vodou symbol of Ogou Feray depicts crossed swords, as seen in this vèvè.
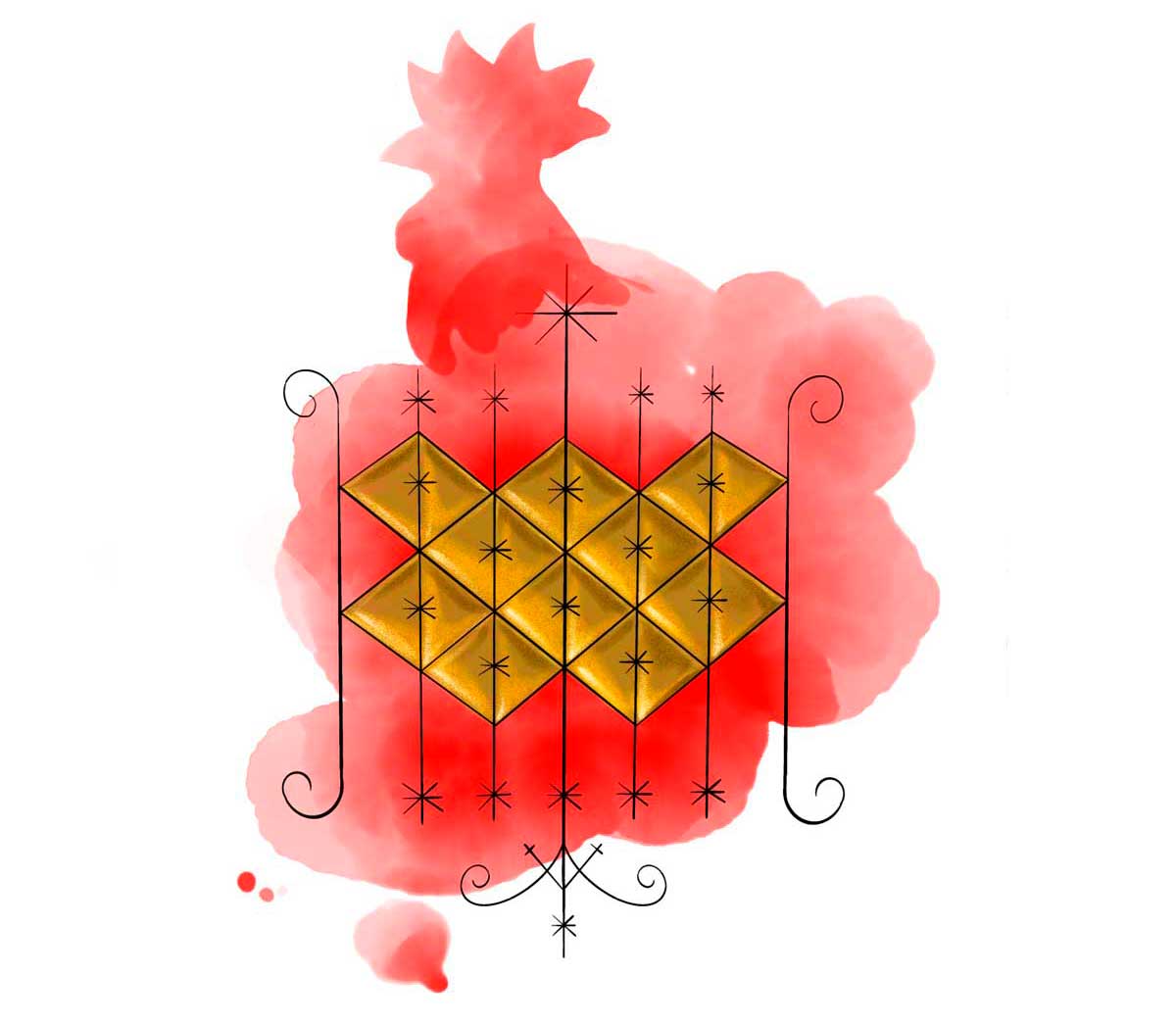
Illustration: Pyelila
The vèvè of Ogou Badagri also shows swords, but here they are intertwined. Ogou is widely revered by Vodou practitioners for his powerful warrior energy. He is often seen as a member of a larger escort of warrior Loas. The swords in the cosmogram symbolize Ogou’s strength and his ability to protect and defend those who call upon him. Whether you’re seeking protection, guidance, or victory in battle, Ogou is a powerful spirit to call upon in Vodou rituals.
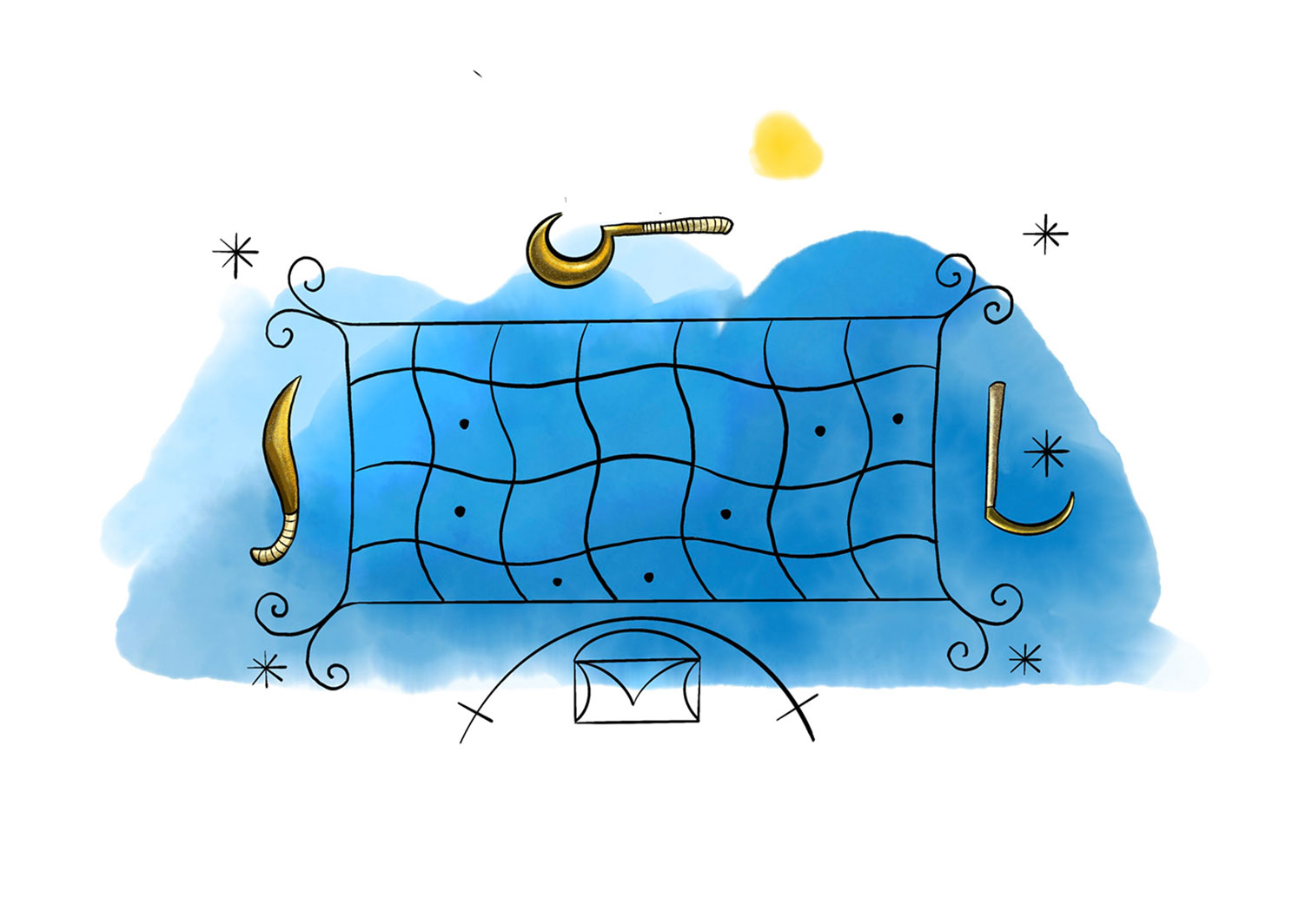

Illustration: Pyelila
Kouzen Zaka: Protector of the Fields
Kouzen Zaka, represented by this vèvè, is the guardian of the fields in Haitian Vodou. The drawing of his symbol showcases elements of agricultural activity, including the earth, machete, sickle, hoe, and a djakout (straw bag). Zaka is closely tied to work and is celebrated on May 1st, the day of the agricultural and labor festival. He is revered by farmers and those who rely on agriculture for their livelihood.
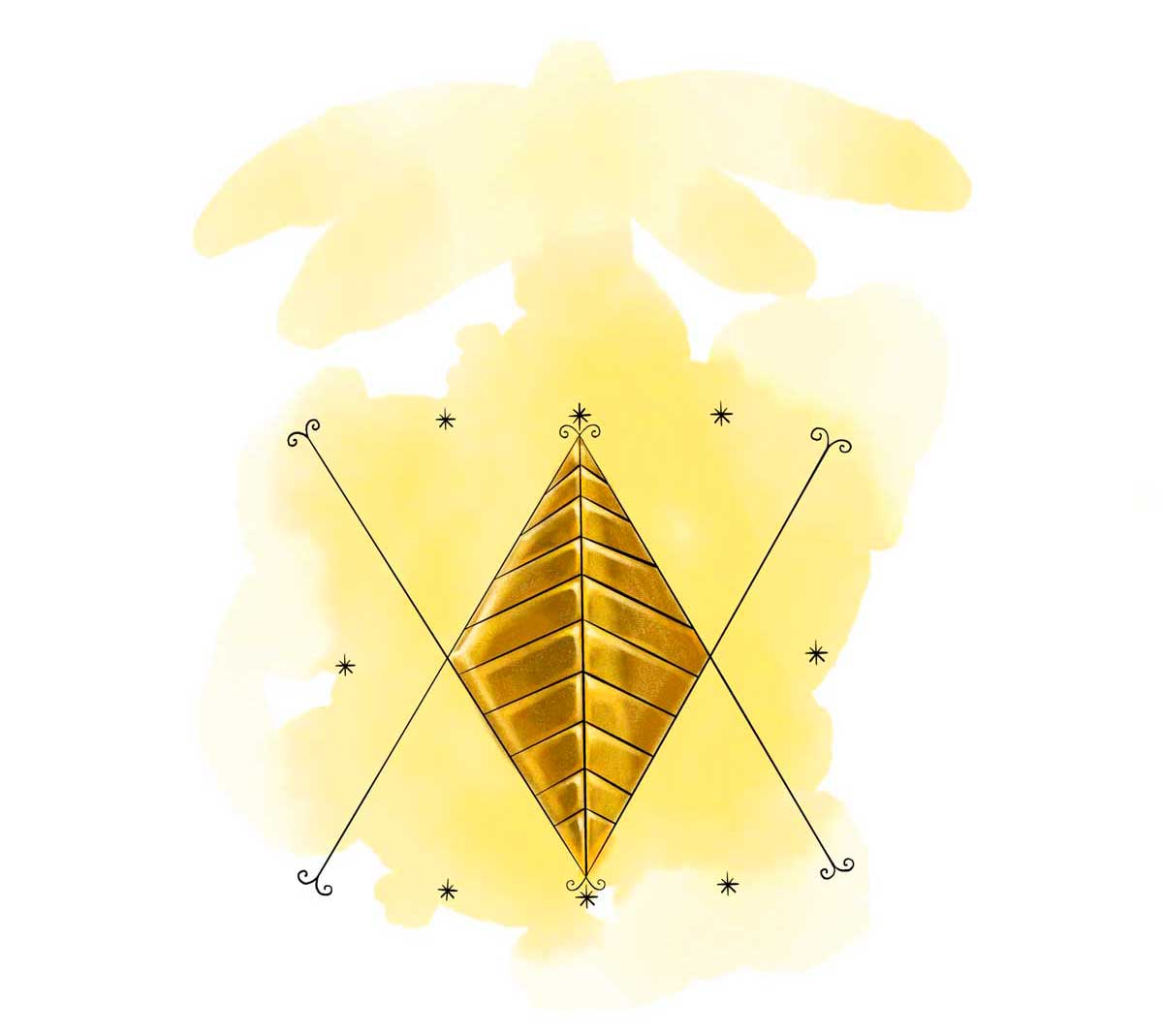
Illustration: Pyelila
Ayizan: The Guardian of Trade and Healing
As the patron of trade and markets, Ayizan is a spirit revered for her powerful healing gifts. Her vèvè comprises four intersecting lines forming a diamond shape in the center. This central diamond symbolizes a palm leaf, which is the preferred tree of this deity. As the patron of commerce and markets, Ayizan is revered by merchants and traders alike.
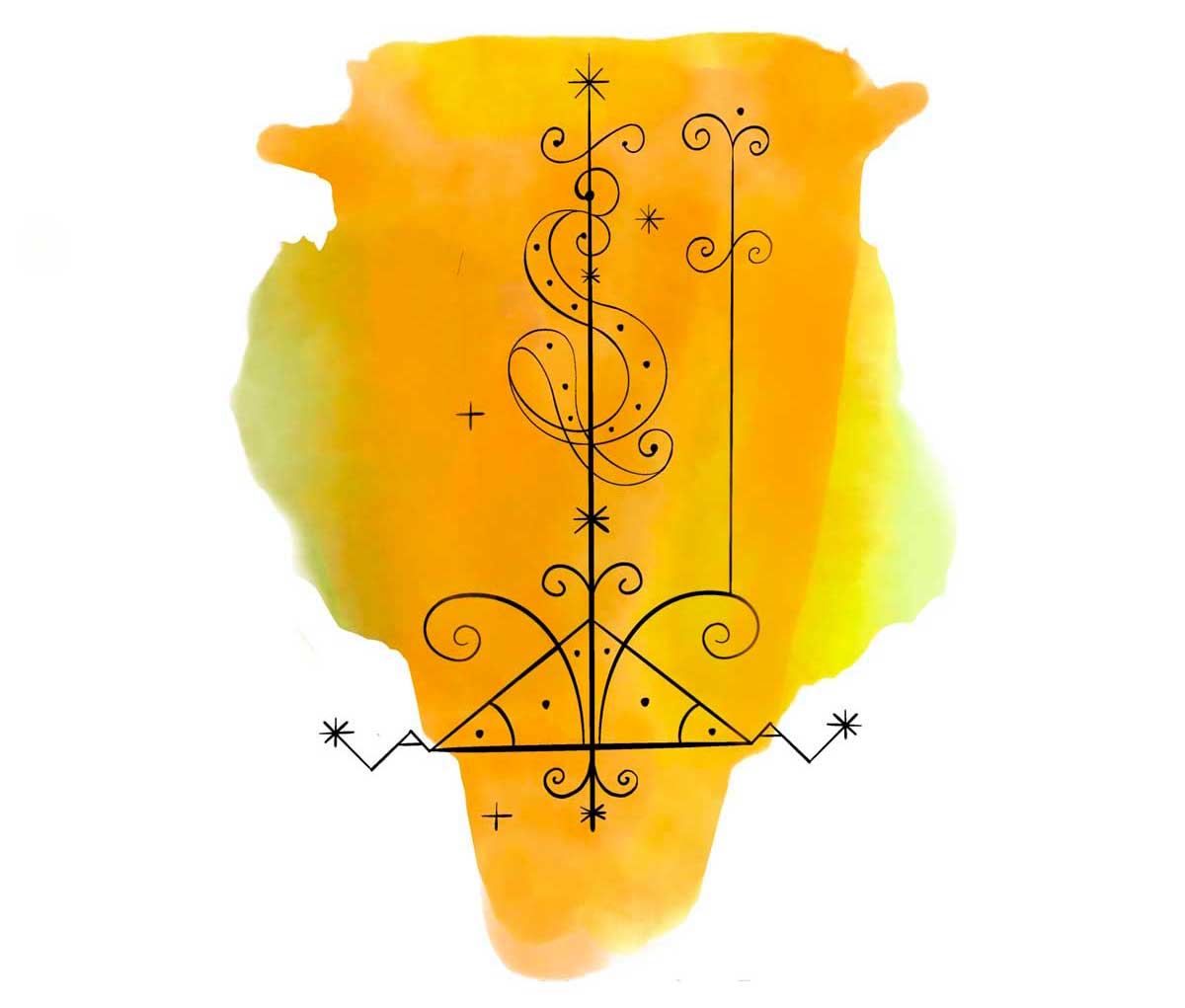
Illustration: Pyelila
Papa Loko: The Keeper of Vodou Traditions
An important spirit in Haitian Vodou, Papa Loko is known for his healing powers and association with the wind. As the first Vodou priest, he is responsible for conferring spiritual powers to new priests and safeguarding the traditions of the religion.
His vèvè, which depicts a snake coiled around a vertical axis and a cane, symbolizes his role as the protector of ounfò, the Vodou temples. Papa Loko is widely respected by practitioners for his influence on preserving the ancient customs and beliefs within Vodou.
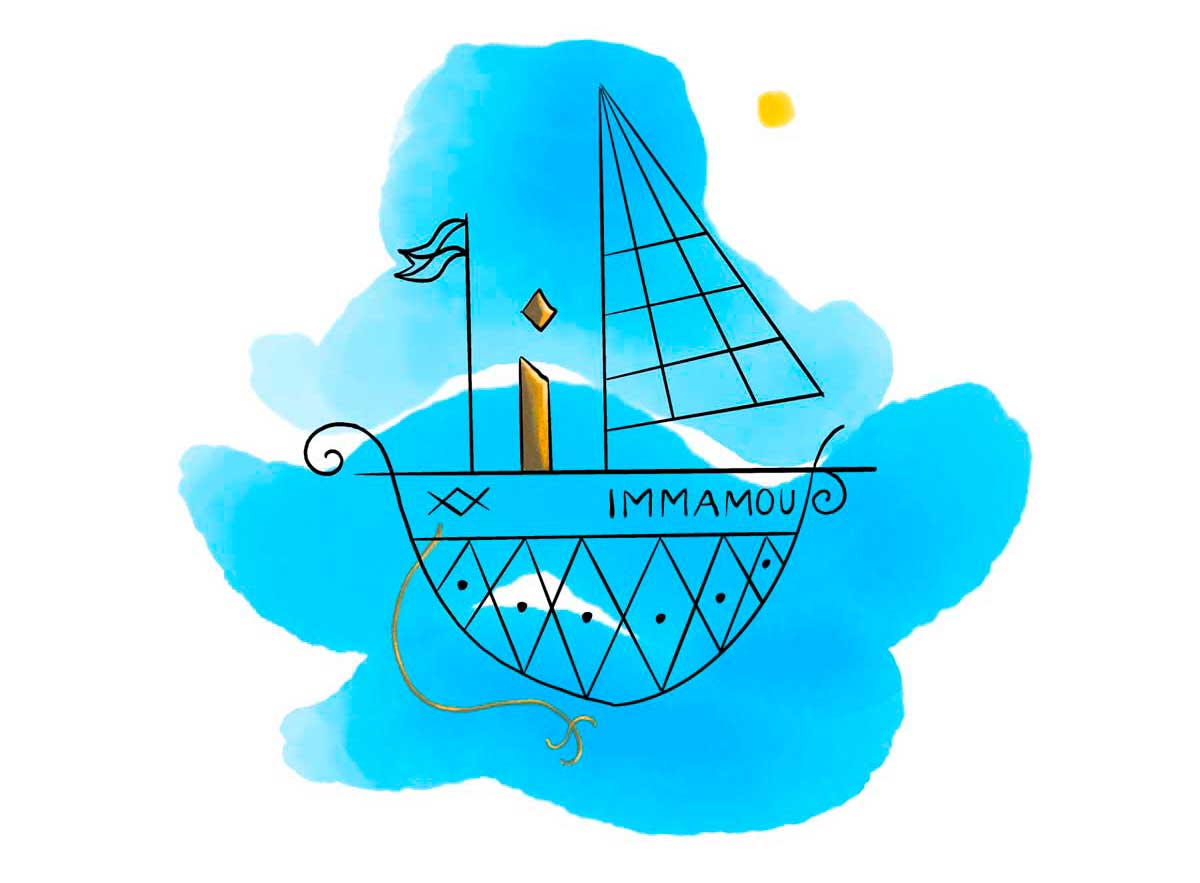
Illustration: Pyelila
Agwe: Master of the Seas
In Haitian Vodou, Agwe, also known as Mèt Agwe, is the ruler of the oceans. His vèvè symbolizes a boat, reflecting his maritime domain. Coastal communities often pay homage to this powerful spirit by offering him devotion in a boat loaded with offerings. For followers of Vodou, the ship in Agwe’s Vodou symbol represents his role in escorting the souls of the deceased to their final resting place.
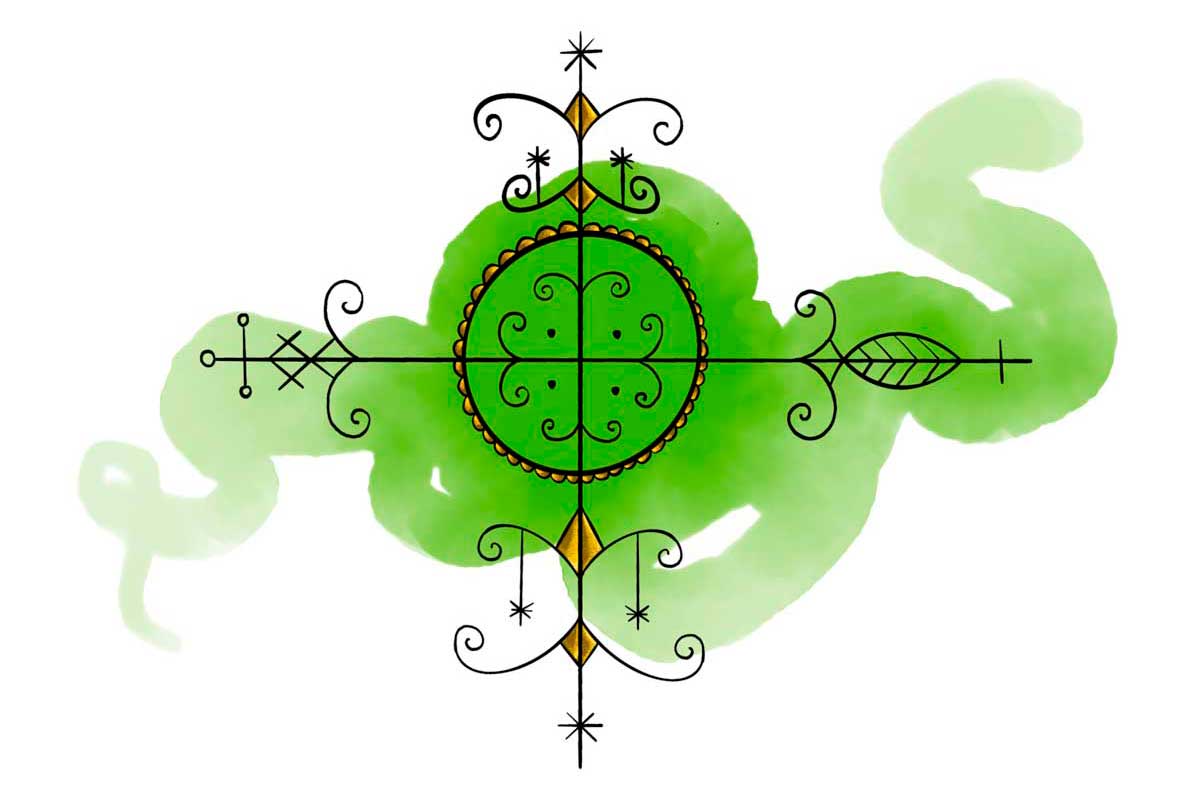
Illustration: Pyelila
Simbi: The Spirit of Water
Simbi spirits are guardians of water sources, rivers, and springs. They are also healing spirits who can grant the gift of clairvoyance to their followers. With the country’s many rivers, waterfalls, and long coastlines, this spirit holds a significant place in the hearts of Haitians, especially in coastal cities where fishing is the main source of income and food.
For boat owners, merchants traveling by sea, and aspiring fishermen, Simbi is of great importance. Some even perform a ceremony before embarking on a journey.
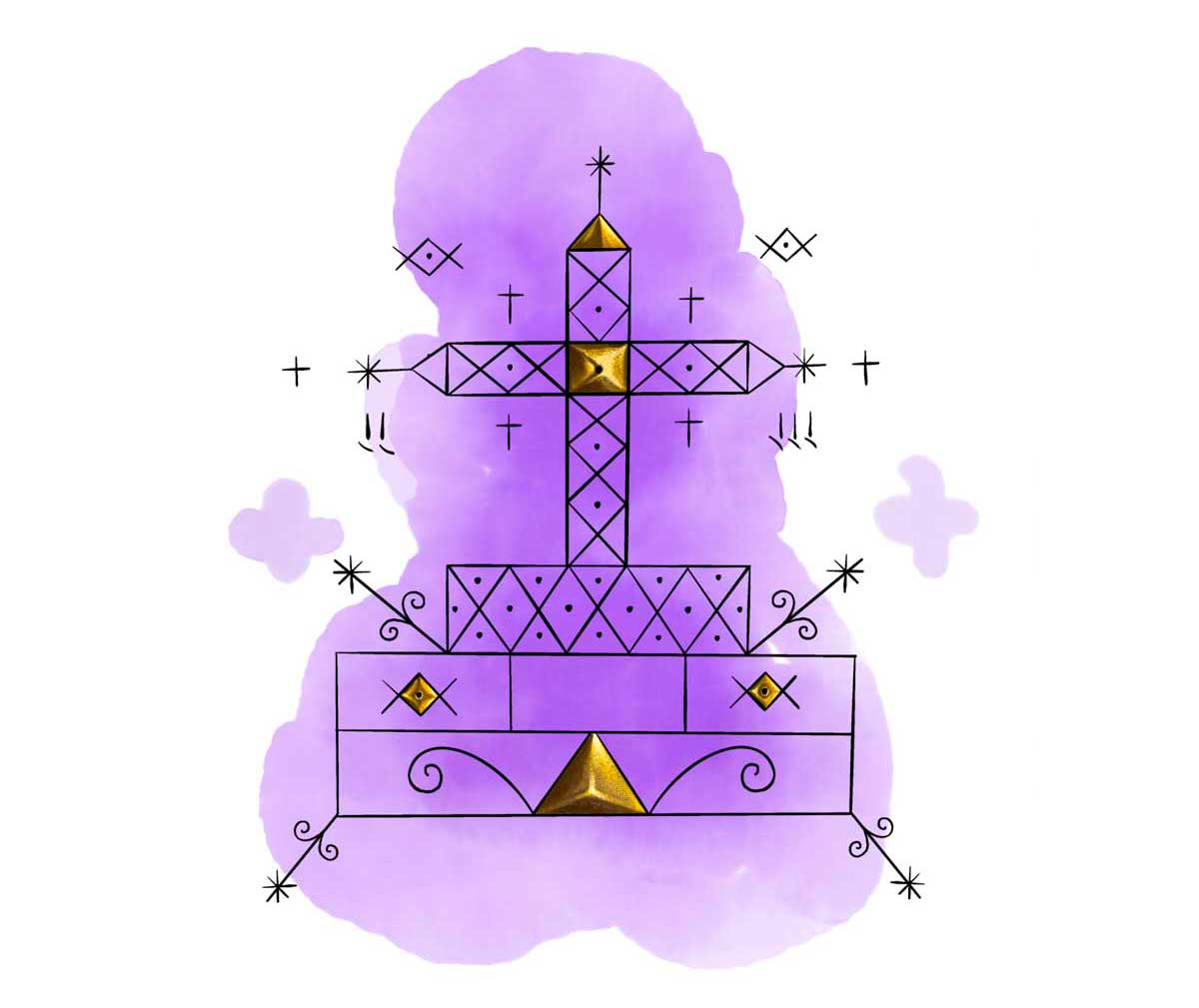
Illustration: Pyelila
Baron Samedi – The Vodou Guardian of Death
Bawon Samedi is the master of cemeteries and the guardian between the world of the dead and the living. His vèvè depicts a tomb with a cross and two coffins, symbolizing death. He is one of the most famous of all Vodou spirits and is followed by an entourage of other spirits known as the Gede.
To gain a deeper understanding of the Gede spirits, check out this story about the Fet Gede celebration in Haiti.
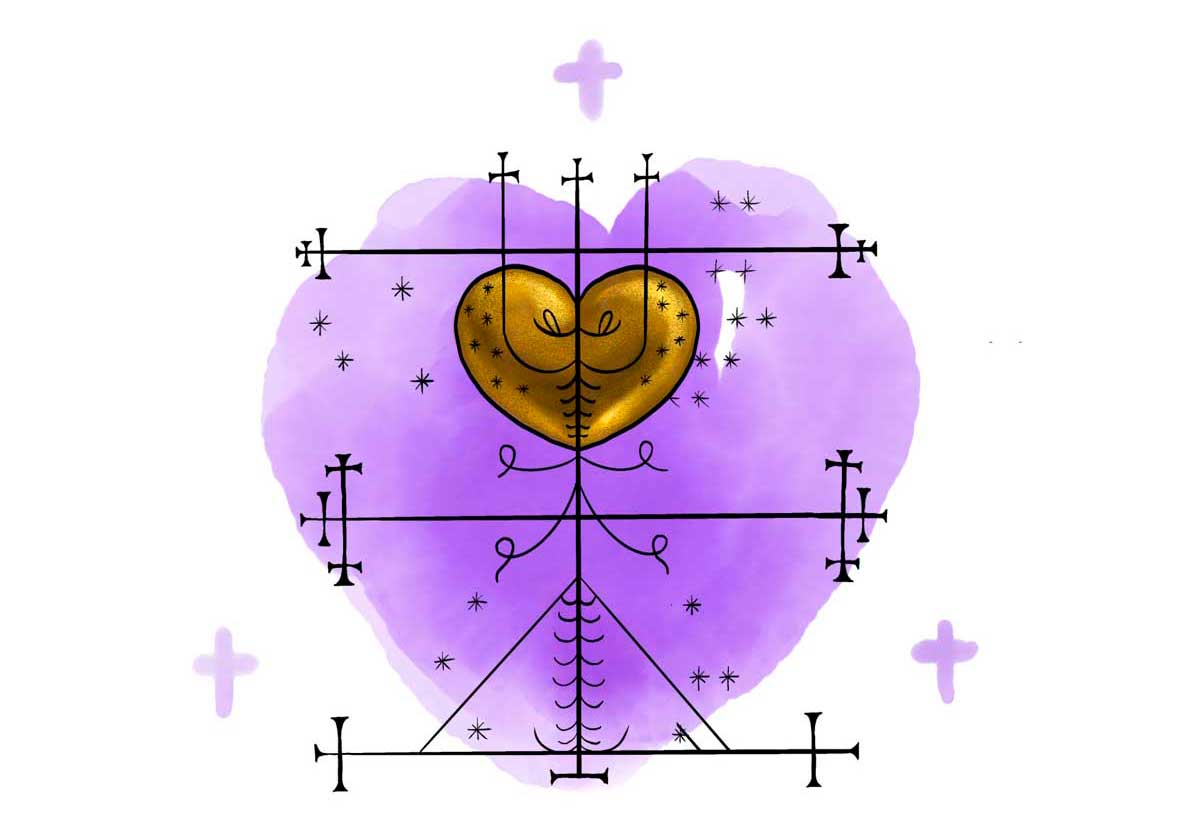
Illustration: Pyelila
Grann Brigitte: The Consort of Baron Samedi
Grann Brigitte forms a couple with Baron Samedi in order to reign over the world of the dead and cemeteries. Her vèvè symbol is made up of three parallel lines, and a heart, all decorated with small crosses.
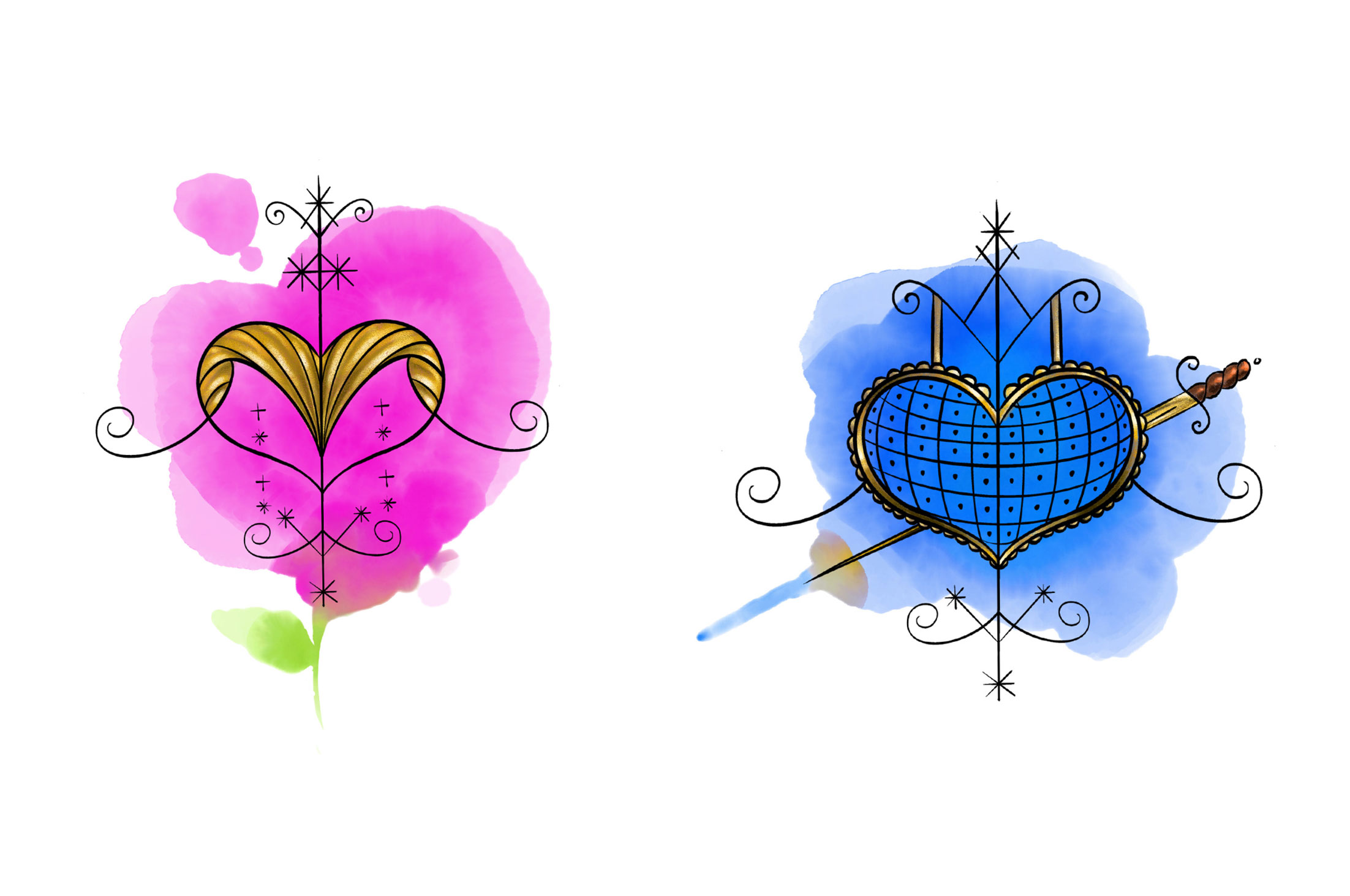
Illustration: Pyelila
Erzulie Freda & Erzulie Dantor: The Heart of Love and Protection
Erzulie Freda and Erzulie Dantor are often considered sisters in Haitian Vodou. They share similarities in their vèvè, but also have distinct differences. Both drawings depict a heart, which represents love, but Dantor’s is pierced by a knife, whereas Freda’s is unbroken. Erzulie Freda is known for her jealousy and unpredictable nature, but also her power as a lover. On the other hand, Erzulie Dantor is revered as a fierce and loving mother figure.
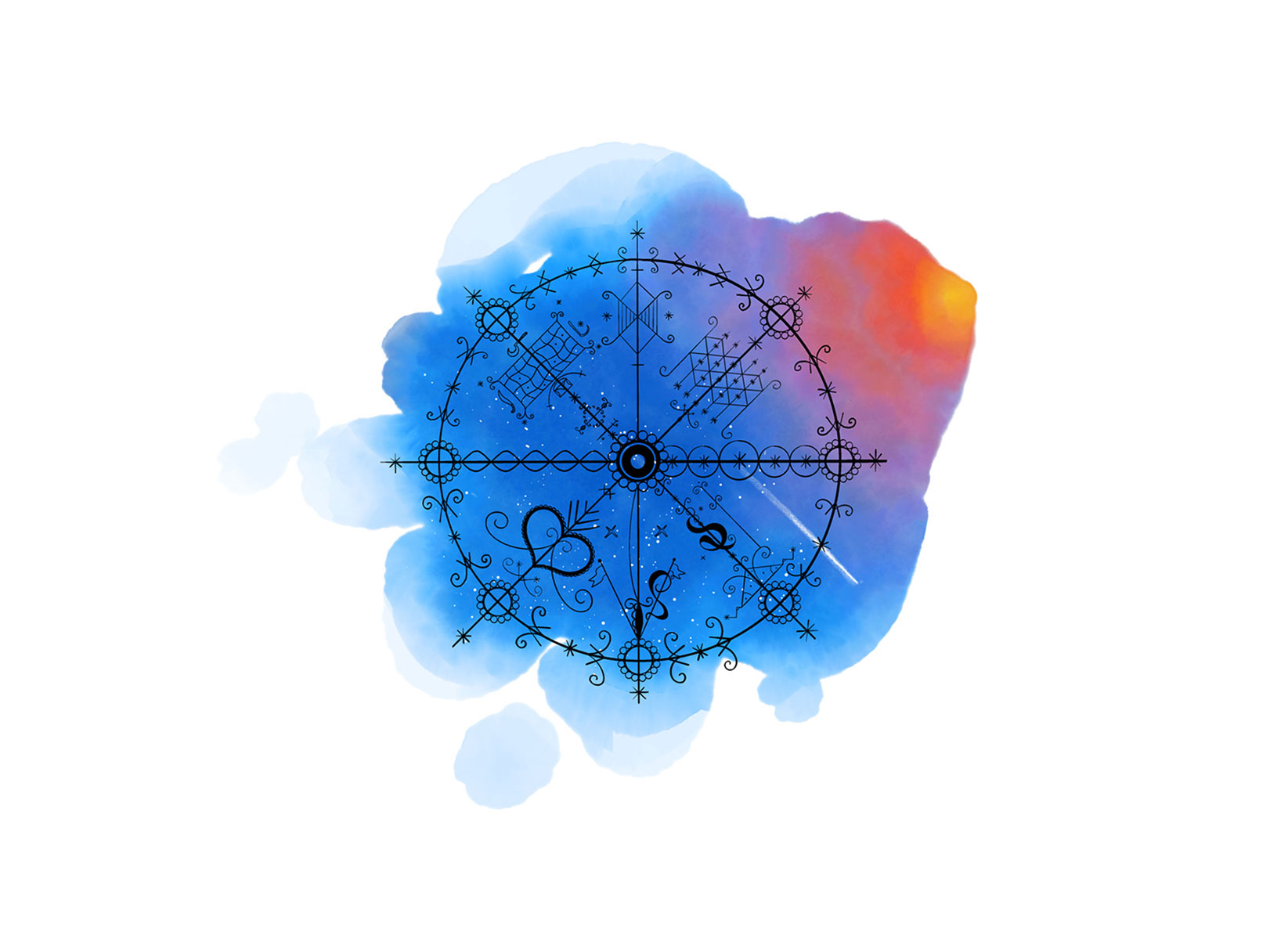

Illustration: Pyelila
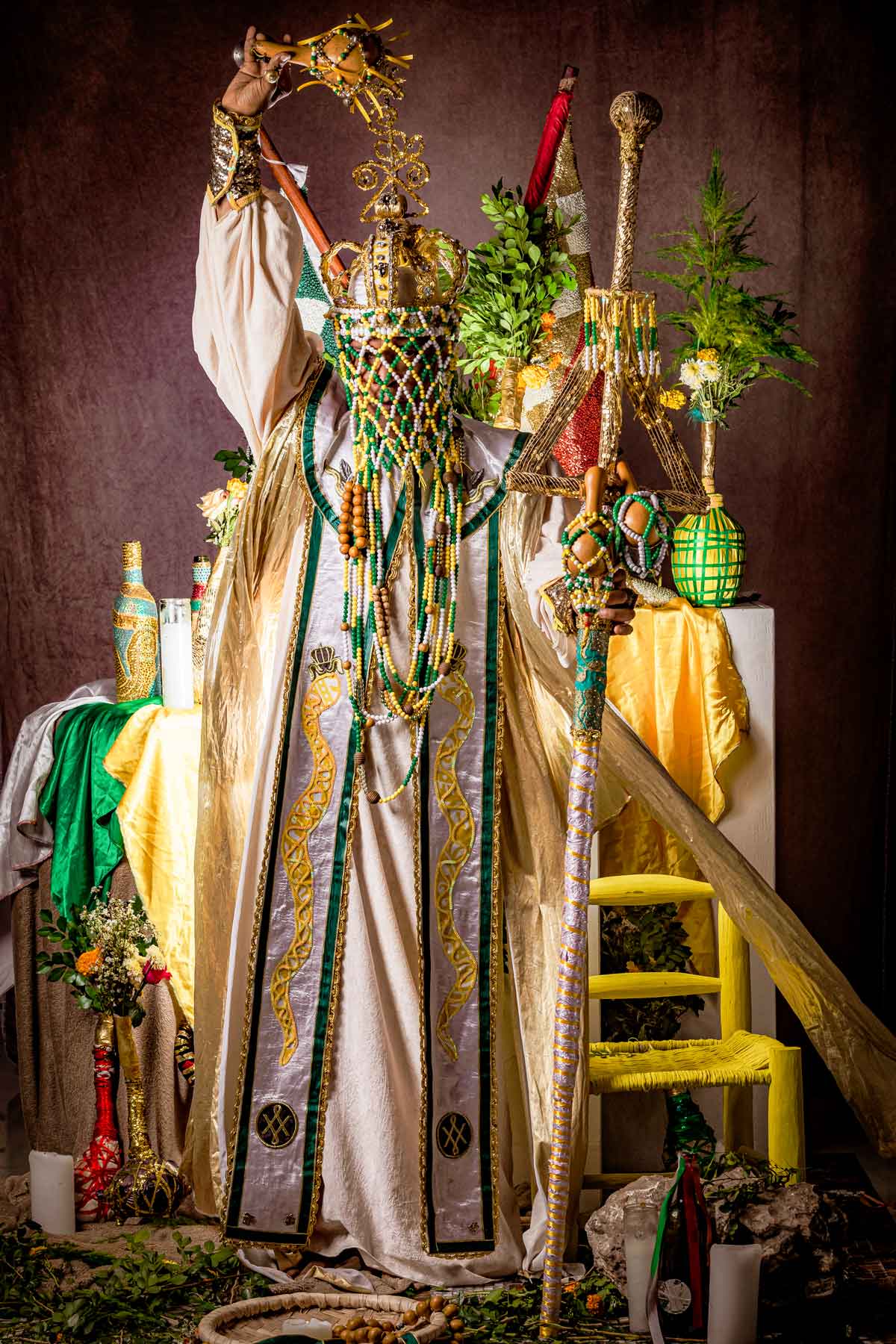
Milokan – The Masterpiece Vèvès
The Milokan vèvè symbols are a display of intricate complexity. They don’t represent a solitary spirit, but a congregation of deities. During Vodou rituals, initiates can call upon multiple spirits simultaneously through the use of Milokan. These vèvè are true works of art, embodying the mastery of their creators.
Vodou vèvè cosmograms are more than just symbols in Haitian culture; it’s an art form, mastered by initiated priests. The intricate drawings are imbued with mystical and ritualistic significance, representing a connection between the human and spirit world.
But the beauty of vèvè extends beyond the realm of spirituality. Its aesthetic appeal has made it a popular trend in fashion and business branding, showcasing the richness of Haitian culture. Entrepreneurs and artists, such as those of the Saint-Soleil painting movement, incorporate vèvè designs into their works, adding a touch of Vodou to their creations.
If you’re interested in learning more about Vodou, its history, and its impact on Haitian society, here are some more stories that delve into this fascinating topic:
- Test your knowledge of the world’s most maligned spiritual tradition by learning how to separate fact from fiction when it comes to Haitian Vodou.
- If you’re interested in exploring the history of this ancestral spiritual practice and its place in Haitian culture consider visiting the Bureau of Ethnology, a museum dedicated to Vodou in Haiti.
- Moreover, you can unlock some of the enduring mysteries about Vodou by walking in the trail of the annual one-of-a-kind Vodou pilgrimage to Saut d’Eau that brings together crowds of the devoted and the curious.
- For further reading, here are some of our favorite books about Haitian Vodou to make room for on your bookshelf.
- Finally, if you have the opportunity to visit Haiti, you could take your exploration of Vodou to the next level by attending a Vodou ceremony to witness its beauty and power first-hand.
Written by Costaguinov Baptiste.
Published March 2023.
Explore Haitian Vodou

Paradise for your inbox
Your monthly ticket to Haiti awaits! Get first-hand travel tips, the latest news, and inspiring stories delivered straight to your inbox—no spam, just paradise.